Page 71 - The engineering of chemical reactions
P. 71
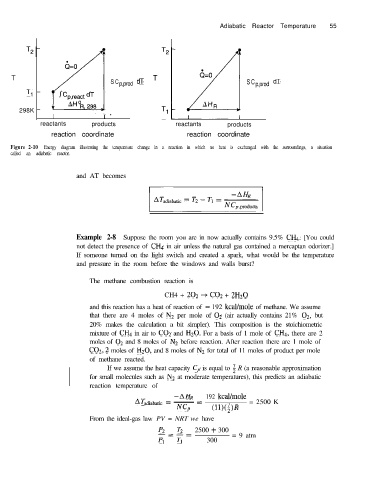
Adiabatic Reactor Temperature 55
T
S C p,prod dT S C p,prod dT
Tl
298K
I I -
reactants products reactants products
reaction coordinate reaction coordinate
Figure 2-10 Energy diagram illustrating the temperature change in a reaction in which no heat is exchanged with the surroundings, a situation
called an adiabatic reactor.
and AT becomes
Example 2-8 Suppose the room you are in now actually contains 9.5% CH4. [You could
not detect the presence of CH4 in air unless the natural gas contained a mercaptan odorizer.]
If someone turned on the light switch and created a spark, what would be the temperature
and pressure in the room before the windows and walls burst?
The methane combustion reaction is
CH4 + 202 + CO2 + 2H20
and this reaction has a heat of reaction of - 192 kcal/mole of methane. We assume
that there are 4 moles of N2 per mole of 02 (air actually contains 21% 02, but
20% makes the calculation a bit simpler). This composition is the stoichiometric
mixture of CH4 in air to CO:! and H20. For a basis of 1 mole of CH4, there are 2
moles of 02 and 8 moles of N2 before reaction. After reaction there are 1 mole of
CO2,2 moles of H20, and 8 moles of N2 for total of 11 moles of product per mole
of methane reacted.
If we assume the heat capacity C, is equal to i R (a reasonable approximation
for small molecules such as N2 at moderate temperatures), this predicts an adiabatic
reaction temperature of
-AH, 192 kcal/mole
ATadiabatic = - = = 2500 K
NC, W)(;)R
From the ideal-gas law PV = NRT we have
T2
f'2
-=-= 2500 + 300 = 9 atm
9 T 300