Page 78 - The engineering of chemical reactions
P. 78
62 Reaction Rates, the Batch Reactor, and the Real World
These reactions are all very endothermic, and heat must be supplied to the retorts or
tube furnaces, not only to heat the reactants to a temperature of 600 to 1000°C where they
will react at an acceptable rate, but also to provide the heat of the reactions, which is several
times the sensible heat.
Sometime in the early twentieth century it was found that if the steel tubes in the
furnace had certain kinds of dirt in them, the cracking reactions were faster and they
produced less methane and coke. These clays were acting as catalysts, and they were
soon made synthetically by precipitating silica and alumina solutions into aluminosilicate
cracking catalysts. The tube furnace+also evolved into a more efficient reactor, which per-
formsJluidized catalytic cracking (FCC), which is now the workhorse reactor in petroleum
refining.
Petroleum refinery
A modern petroleum refinery in the United States processes between 100,000 and 500,000
barrels/day of crude oil. The incoming crude is first desalted and then passed through an
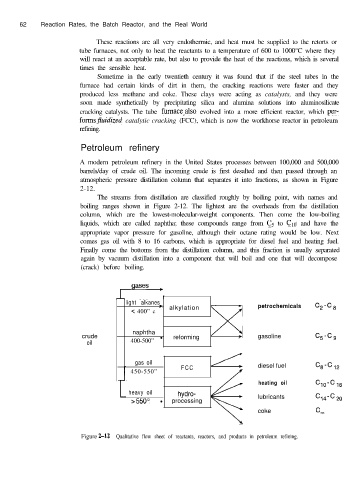
atmospheric pressure distillation column that separates it into fractions, as shown in Figure
2-12.
The streams from distillation are classified roughly by boiling point, with names and
boiling ranges shown in Figure 2-12. The lightest are the overheads from the distillation
column, which are the lowest-molecular-weight components. Then come the low-boiling
liquids, which are called naphtha; these compounds range from C5 to C!to and have the
appropriate vapor pressure for gasoline, although their octane rating would be low. Next
comes gas oil with 8 to 16 carbons, which is appropriate for diesel fuel and heating fuel.
Finally come the bottoms from the distillation column, and this fraction is usually separated
again by vacuum distillation into a component that will boil and one that will decompose
(crack) before boiling.
light alkanes petrochemicals
< 400” c * alkylation
naphtha
crude l reforming gasoline
oil 400-500”
gas oil
FCC diesel fuel
450-550”
heating oil
heavy oil hydro- lubricants
2.550” l processing
coke
Figure 2-12 Qualitative flow sheet of reactants, reactors, and products in petroleum refining.