Page 79 - The engineering of chemical reactions
P. 79
Petroleum Refining 63
Crude oils vary greatly in boiling range and types of molecular structures. The best
now comes only from the Middle East and is mostly naphtha that needs little refining. The
worst now comes from the United States, is very high molecular weight, and consists largely
of polyaromatic compounds containing S, N, and heavy metals, particularly V and Ni. The
C:H ratio of these ranges also varies from perhaps 1:3 for light fractions to 1: 1 for vacuum
residual oil.
The task of the refinery is to turn crude oil into valuable products. The demands for
products vary greatly with region and with season. The Gulf Coast needs more petrochemical
feedstocks, while the Upper Midwest needs more heating fuel. Gasoline accounts for
approximately one-half of the total petroleum used in the United States, but demand for
gasoline is highest in the spring and summer vacation season.
These fractions from primary distillation are sent to reactors to crack them further
and isomerize them into products with more value, such as gasoline and petrochemicals.
The refinery is a massive blending system in which streams into and out of reactors are
recycled and blended into products with the desired properties and amounts.
There are basically four types of reactors in refining. Fluidized catalytic cracking
reactors process perhaps 30% of all the crude, the gas oil fraction. The heavier fraction
must have hydrogen added, and these processes are called hydroprocessing. Gasoline must
have certain isomers for octane rating, and this is done in catalytic reforming. Some products
have too low a molecular weight and must be recombined into larger molecules, a process
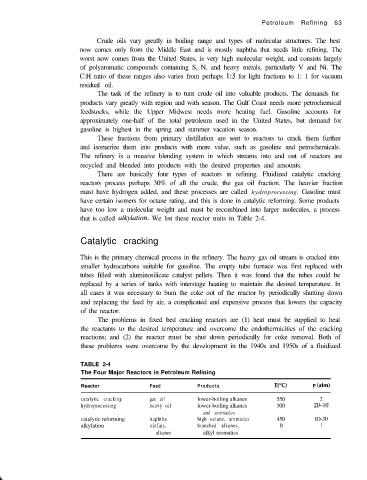
that is called alkylution. We list these reactor units in Table 2-4.
Catalytic cracking
This is the primary chemical process in the refinery. The heavy gas oil stream is cracked into
smaller hydrocarbons suitable for gasoline. The empty tube furnace was first replaced with
tubes filled with aluminosilicate catalyst pellets. Then it was found that the tubes could be
replaced by a series of tanks with interstage heating to maintain the desired temperature. In
all cases it was necessary to bum the coke out of the reactor by periodically shutting down
and replacing the feed by air, a complicated and expensive process that lowers the capacity
of the reactor.
The problems in fixed bed cracking reactors are (1) heat must be supplied to heat
the reactants to the desired temperature and overcome the endothermicities of the cracking
reactions; and (2) the reactor must be shut down periodically for coke removal. Both of
these problems were overcome by the development in the 1940s and 1950s of a fluidized
TABLE 2-4
The Four Major Reactors in Petroleum Refining
Reactor Feed Products -u”C) P (atm)
catalytic cracking gas oil lower-boiling alkanes 550 2
hydroprocessing heavy oil lower-boiling alkanes 500 20-10
and aromatics
catalytic reforming naphtha high octane, aromatics 450 IO-30
alkylation olefins, branched alkanes, 0 1
alkanes alkyl aromatics