Page 84 - The engineering of chemical reactions
P. 84
68 Reaction Rates, the Batch Reactor, and the Real World
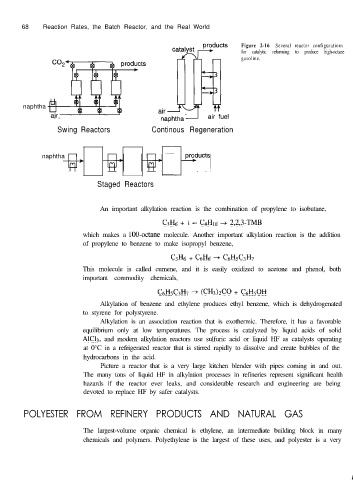
Figure 2-16 Several reactor configurations
for catalytic reforming to produce high-octane
gasoline.
naphtha
Swing Reactors Continous Regeneration
naphtha n
*
Staged Reactors
An important alkylation reaction is the combination of propylene to isobutane,
C3Hs + i - C,HIO -+ 2,2,3-TMB
which makes a loo-octane molecule. Another important alkylation reaction is the addition
of propylene to benzene to make isopropyl benzene,
C3H6 + C& + CrjH&H7
This molecule is called cumene, and it is easily oxidized to acetone and phenol, both
important commodity chemicals,
c&c& -+ (CH&CO + C6H@H
Alkylation of benzene and ethylene produces ethyl benzene, which is dehydrogenated
to styrene for polystyrene.
Alkylation is an association reaction that is exothermic. Therefore, it has a favorable
equilibrium only at low temperatures. The process is catalyzed by liquid acids of solid
AlC13, and modern alkylation reactors use sulfuric acid or liquid HF as catalysts operating
at 0°C in a refrigerated reactor that is stirred rapidly to dissolve and create bubbles of the
hydrocarbons in the acid.
Picture a reactor that is a very large kitchen blender with pipes coming in and out.
The many tons of liquid HF in alkylation processes in refineries represent significant health
hazards if the reactor ever leaks, and considerable research and engineering are being
devoted to replace HF by safer catalysts.
POLYESTER FROM REFINERY PRODUCTS AND NATURAL GAS
The largest-volume organic chemical is ethylene, an intermediate building block in many
chemicals and polymers. Polyethylene is the largest of these uses, and polyester is a very