Page 259 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 259
0066_frame_C12 Page 24 Wednesday, January 9, 2002 4:22 PM
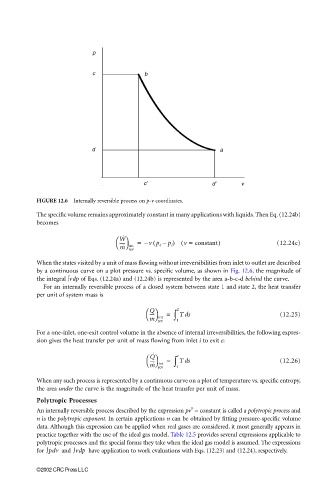
FIGURE 12.6 Internally reversible process on p-v coordinates.
The specific volume remains approximately constant in many applications with liquids. Then Eq. (12.24b)
becomes
˙
W
= – vp e – ) ( v = constant) (12.24c)
(
-----
int p i
m ˙
rev
When the states visited by a unit of mass flowing without irreversibilities from inlet to outlet are described
by a continuous curve on a plot pressure vs. specific volume, as shown in Fig. 12.6, the magnitude of
the integral ∫vdp of Eqs. (12.24a) and (12.24b) is represented by the area a-b-c-d behind the curve.
For an internally reversible process of a closed system between state 1 and state 2, the heat transfer
per unit of system mass is
∫ 2 Ts (12.25)
Q
----
d
int = 1
m
rev
For a one-inlet, one-exit control volume in the absence of internal irreversibilities, the following expres-
sion gives the heat transfer per unit of mass flowing from inlet i to exit e:
˙
e
Q
int ∫ Ts (12.26)
=
----
d
m ˙
rev i
When any such process is represented by a continuous curve on a plot of temperature vs. specific entropy,
the area under the curve is the magnitude of the heat transfer per unit of mass.
Polytropic Processes
n
An internally reversible process described by the expression pv = constant is called a polytropic process and
n is the polytropic exponent. In certain applications n can be obtained by fitting pressure-specific volume
data. Although this expression can be applied when real gases are considered, it most generally appears in
practice together with the use of the ideal gas model. Table 12.5 provides several expressions applicable to
polytropic processes and the special forms they take when the ideal gas model is assumed. The expressions
for ∫pvd and ∫vpd have application to work evaluations with Eqs. (12.23) and (12.24), respectively.
©2002 CRC Press LLC