Page 65 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 65
5.2 Microactuators
Electrostatic Actuation
The most widely utilized multicomponent microactuators are those based upon electrostatic transduc-
tion. These actuators can also be regarded as a variable capacitance type, since they operate in an
analogous mode to variable reluctance type electromagnetic actuators (e.g., variable reluctance stepper
motors). Electrostatic actuators have been developed in both linear and rotary forms. The two most
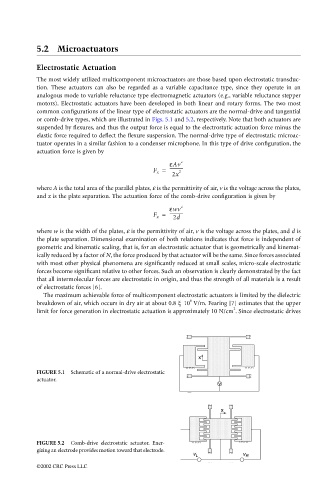
common configurations of the linear type of electrostatic actuators are the normal-drive and tangential
or comb-drive types, which are illustrated in Figs. 5.1 and 5.2, respectively. Note that both actuators are
suspended by flexures, and thus the output force is equal to the electrostatic actuation force minus the
elastic force required to deflect the flexure suspension. The normal-drive type of electrostatic microac-
tuator operates in a similar fashion to a condenser microphone. In this type of drive configuration, the
actuation force is given by
2
εAv
F x = ------------
2
2x
where A is the total area of the parallel plates, ε is the permittivity of air, v is the voltage across the plates,
and x is the plate separation. The actuation force of the comb-drive configuration is given by
2
εwv
F x = ------------
2d
where w is the width of the plates, ε is the permittivity of air, v is the voltage across the plates, and d is
the plate separation. Dimensional examination of both relations indicates that force is independent of
geometric and kinematic scaling, that is, for an electrostatic actuator that is geometrically and kinemat-
ically reduced by a factor of N, the force produced by that actuator will be the same. Since forces associated
with most other physical phenomena are significantly reduced at small scales, micro-scale electrostatic
forces become significant relative to other forces. Such an observation is clearly demonstrated by the fact
that all intermolecular forces are electrostatic in origin, and thus the strength of all materials is a result
of electrostatic forces [6].
The maximum achievable force of multicomponent electrostatic actuators is limited by the dielectric
6
breakdown of air, which occurs in dry air at about 0.8 x 10 V/m. Fearing [7] estimates that the upper
2
limit for force generation in electrostatic actuation is approximately 10 N/cm . Since electrostatic drives
FIGURE 5.1 Schematic of a normal-drive electrostatic
actuator.
FIGURE 5.2 Comb-drive electrostatic actuator. Ener-
gizing an electrode provides motion toward that electrode.
©2002 CRC Press LLC