Page 186 - Thermal Hydraulics Aspects of Liquid Metal Cooled Nuclear Reactors
P. 186
158 Thermal Hydraulics Aspects of Liquid Metal Cooled Nuclear Reactors
Lead
Sodium
Lead-lithium
Prandtl number (–)
Temperature (°C)
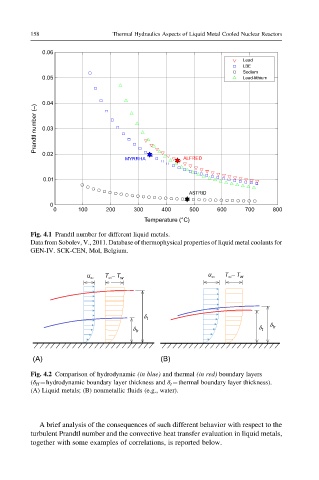
Fig. 4.1 Prandtl number for different liquid metals.
Data from Sobolev, V., 2011. Database of thermophysical properties of liquid metal coolants for
GEN-IV. SCK-CEN, Mol, Belgium.
u ¥ T – T w u ¥ T ¥ – T w
¥
d t
d h d t d h
(A) (B)
Fig. 4.2 Comparison of hydrodynamic (in blue) and thermal (in red) boundary layers
(δ H ¼hydrodynamic boundary layer thickness and δ t ¼thermal boundary layer thickness).
(A) Liquid metals; (B) nonmetallic fluids (e.g., water).
A brief analysis of the consequences of such different behavior with respect to the
turbulent Prandtl number and the convective heat transfer evaluation in liquid metals,
together with some examples of correlations, is reported below.