Page 350 - Thermodynamics of Biochemical Reactions
P. 350
350 Mathernatica Solutions to Problems
This is the equilibrium pressure in bars for an ideal 1 M solution of carbondioxide as a function of temperature. The equilib-
rium pressure increases with the temperature. This is Fig. 8.1.
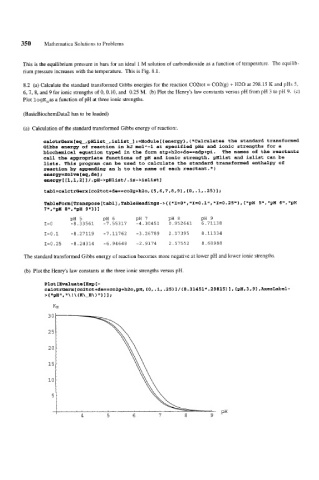
8.2 (a) Calculate the standard transformed Gibbs energies for the reaction C02tot = C02(g) + H20 at 298.15 K and pHs 5,
6,7, 8, and 9 €or ionic strengths of 0, 0.10, and 0.25 M. (b) Plot the Henry's law constants versus pH from pH 3 to pH 9. (c)
Plot logK,as a function of pH at three ionic strengths.
(BasicBiochemData2 has to be loaded)
(a) Calculation of the standard transformed Gibbs energy of reaction:.
calctrGerx[e~,pHlist_,islist_l:=Module[{energy},(*Calculates the standard transformed
Gibbs energy of reaction in kJ molA-1 at specified pHs and ionic strengths for a
biochemical equation typed in the fom atp+hao+de==adp+pi. The names of the reactants
call the appropriate functions of pH and ionic strength. pHlist and islist can be
lists. This program can be used to calculate the standard transformed enthalpy of
reaction by appending an h to the name of each reactant.*)
energy=Solve [eq,deI;
energy~[l,l,2]]/.pH->pH~~St/.iS->is~~St]
TableForm [Transpose [ tab11 , TableHeadings-> { { mlI=O1l, "I=O. 1" , "I=O. 25 'I 1, E "pH 5", "pH 6", I'pH
7","pH 8","pH 9"))1
PH 5 PH 6 PH 7 PH 8 PH 9
I=O -8.33561 -7.55317 -4.30451 0.952641 6.71138
I=O.1 -8.27119 -7.11762 -3.26789 2.17395 8.11334
I=O.25 -8.24314 -6.94648 -2.9174 2.57552 8.60988
The standard transformed Gibbs energy of reaction becomes more negative at lower pH and lower ionic strengths.
(b) Plot the Henry's law constants at the three ionic strengths versus pH.
Plot [hraluate CExp C-
ca1ctrGerx[co2tot+de==co2g+h2o,pH,{0,.1,.25~1~~8.31451*.29815~1,~pH,3,9~,~esLab~~-
> { '*pH", ! \ (K\-H\ ) 'I 1 I 1 ;
KH