Page 318 - Tunable Lasers Handbook
P. 318
278 Norman P. Barnes
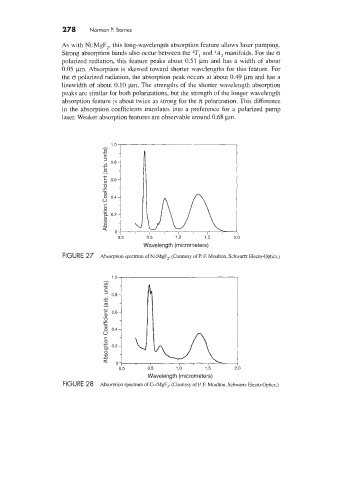
As with Ni:MgF,, this long-wavelength absorption feature allows laser pumping.
Strong absorption bands also occur between the T, and qA, manifolds. For the rs
polarized radiation, this feature peaks about 0.51 pm andhas a width of about
0.05 pm. Absorption is skewed toward shorter wavelengths for this feature. For
the rs polarized radiation, the absorption peak occurs at about 0.49 pm and has a
linewidth of about 0.10 pm. The strengths of the shorter wavelength absorption
peaks are similar for both polarizations, but the strength of the longer wavelength
absorption feature is about twice as strong for the n polarization. This difference
in the absorption coefficients translates into a preference for a polarized pump
laser. Weaker absorption features are observable around 0.68 pm.
0.0 0.5 1 .o 1.5 3
Wavelength (micrometers)
FIGURE 27 Absorption spectrum of Ni:hfgFF2. (Courtesy of P. E hloulton, Schwartz Electo-Optics)
1 .o
h
(0
+ -
.-
C
0.8-
4
m -
u
+
C 0.6-
._
a,
0
._
c
c
a,
0 0.4-
0
c
0
.-
+
a 0.2-
i
Q
Q o--
0
Wavelength (micrometers)
FIGURE 28 Absorption spectrum of Co:hlgFF2. (Courtesy of P. F. Moulton. Schwartz Electo-Optics.)