Page 58 - Urban water supply handbook
P. 58
URBAN WATER INFRASTRUCTURE: A HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE
URBAN WATER INFRASTRUCTURE 1.57
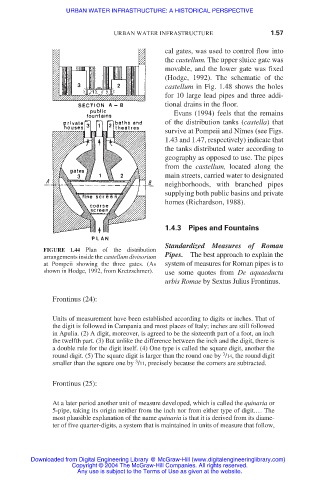
cal gates, was used to control flow into
the castellum. The upper sluice gate was
movable, and the lower gate was fixed
(Hodge, 1992). The schematic of the
castellum in Fig. 1.48 shows the holes
for 10 large lead pipes and three addi-
tional drains in the floor.
Evans (1994) feels that the remains
of the distribution tanks (castella) that
survive at Pompeii and Nîmes (see Figs.
1.43 and 1.47, respectively) indicate that
the tanks distributed water according to
geography as opposed to use. The pipes
from the castellum, located along the
main streets, carried water to designated
neighborhoods, with branched pipes
supplying both public basins and private
homes (Richardson, 1988).
1.4.3 Pipes and Fountains
Standardized Measures of Roman
FIGURE 1.44 Plan of the distribution
arrangements inside the castellum divisorium Pipes. The best approach to explain the
at Pompeii showing the three gates. (As system of measures for Roman pipes is to
shown in Hodge, 1992, from Kretzschmer). use some quotes from De aquaeductu
urbis Romae by Sextus Julius Frontinus.
Frontinus (24):
Units of measurement have been established according to digits or inches. That of
the digit is followed in Campania and most places of Italy; inches are still followed
in Apulia. (2) A digit, moreover, is agreed to be the sixteenth part of a foot, an inch
the twelfth part. (3) But unlike the difference between the inch and the digit, there is
a double rule for the digit itself. (4) One type is called the square digit, another the
3
round digit. (5) The square digit is larger than the round one by /14, the round digit
3
smaller than the square one by /11, precisely because the corners are subtracted.
Frontinus (25):
At a later period another unit of measure developed, which is called the quinaria or
5-pipe, taking its origin neither from the inch nor from either type of digit.… The
most plausible explanation of the name quinaria is that it is derived from its diame-
ter of five quarter-digits, a system that is maintained in units of measure that follow,
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.