Page 213 -
P. 213
Chapter 5 Database Processing
212
to coordinate the activities of users who know nothing about one another. Locking brings its own
set of problems, however, and those problems must be addressed as well. We will not delve further
into this topic here, however.
Be aware of possible data conflicts when you manage business activities that involve multi-user
processing. If you find inaccurate results that seem not to have a cause, you may be experiencing
multi-user data conflicts. Contact your IS department for assistance.
Q5-5 How Are Data Models Used for Database
Development?
In Chapter 12, we will describe the process for developing information systems in detail. However, busi-
ness professionals have such a critical role in the development of database applications that we need to
anticipate part of that discussion here by introducing two topics—data modeling and database design.
Because the design of the database depends entirely on how users view their business environ-
ment, user involvement is critical for database development. Think about the Student database. What
data should it contain? Possibilities are: Students, Classes, Grades, Emails, Office_Visits, Majors, Advis-
ers, Student_Organizations—the list could go on and on. Further, how much detail should be included
in each? Should the database include campus addresses? Home addresses? Billing addresses?
In fact, there are unlimited possibilities, and the database developers do not and cannot know
what to include. They do know, however, that a database must include all the data necessary for the
users to perform their jobs. Ideally, it contains that amount of data and no more. So, during database
development, the developers must rely on the users to tell them what to include in the database.
Database structures can be complex, in some cases very complex. So, before building the data-
base the developers construct a logical representation of database data called a data model. It
describes the data and relationships that will be stored in the database. It is akin to a blueprint. Just
as building architects create a blueprint before they start building, so, too, database developers cre-
ate a data model before they start designing the database.
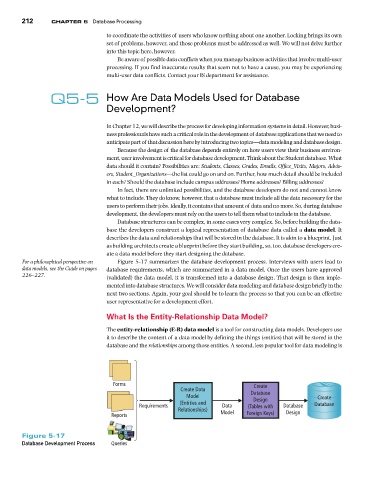
For a philosophical perspective on Figure 5-17 summarizes the database development process. Interviews with users lead to
data models, see the Guide on pages database requirements, which are summarized in a data model. Once the users have approved
226–227. (validated) the data model, it is transformed into a database design. That design is then imple-
mented into database structures. We will consider data modeling and database design briefly in the
next two sections. Again, your goal should be to learn the process so that you can be an effective
user representative for a development effort.
What Is the Entity-Relationship Data Model?
The entity-relationship (E-R) data model is a tool for constructing data models. Developers use
it to describe the content of a data model by defining the things (entities) that will be stored in the
database and the relationships among those entities. A second, less popular tool for data modeling is
Forms Create
Create Data Database
Model Design Create
Requirements (Entities and Data (Tables with Database Database
Relationships) Model Design
Reports Foreign Keys)
Figure 5-17
Database Development Process Queries