Page 305 -
P. 305
Chapter 7 Processes, Organizations, and Information Systems
304
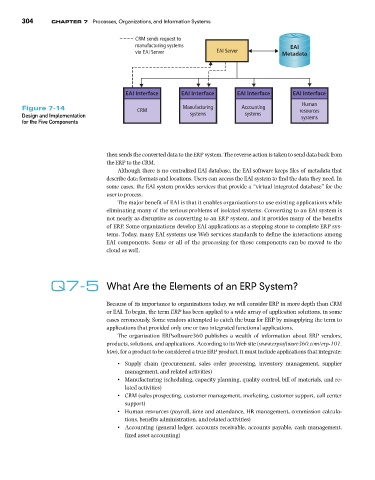
CRM sends request to
manufacturing systems '#+
via EAI Server EAI Server /GVCFCVC
'#+ +PVGTHCEG '#+ +PVGTHCEG '#+ +PVGTHCEG '#+ +PVGTHCEG
Human
Figure 7-14 CRM Manufacturing Accounting resources
Design and Implementation systems systems systems
for the Five Components
then sends the converted data to the ERP system. The reverse action is taken to send data back from
the ERP to the CRM.
Although there is no centralized EAI database, the EAI software keeps files of metadata that
describe data formats and locations. Users can access the EAI system to find the data they need. In
some cases, the EAI system provides services that provide a “virtual integrated database” for the
user to process.
The major benefit of EAI is that it enables organizations to use existing applications while
eliminating many of the serious problems of isolated systems. Converting to an EAI system is
not nearly as disruptive as converting to an ERP system, and it provides many of the benefits
of ERP. Some organizations develop EAI applications as a stepping stone to complete ERP sys-
tems. Today, many EAI systems use Web services standards to define the interactions among
EAI components. Some or all of the processing for those components can be moved to the
cloud as well.
Q7-5 What Are the Elements of an ERP System?
Because of its importance to organizations today, we will consider ERP in more depth than CRM
or EAI. To begin, the term ERP has been applied to a wide array of application solutions, in some
cases erroneously. Some vendors attempted to catch the buzz for ERP by misapplying the term to
applications that provided only one or two integrated functional applications.
The organization ERPsoftware360 publishes a wealth of information about ERP vendors,
products, solutions, and applications. According to its Web site (www.erpsoftware360.com/erp-101.
htm), for a product to be considered a true ERP product, it must include applications that integrate:
• Supply chain (procurement, sales order processing, inventory management, supplier
management, and related activities)
• Manufacturing (scheduling, capacity planning, quality control, bill of materials, and re-
lated activities)
• CRM (sales prospecting, customer management, marketing, customer support, call center
support)
• Human resources (payroll, time and attendance, HR management, commission calcula-
tions, benefits administration, and related activities)
• Accounting (general ledger, accounts receivable, accounts payable, cash management,
fixed asset accounting)