Page 300 -
P. 300
Q7-4 How Do CRM, ERP, and EAI Support Enterprise Processes?
+PDQWPF /CPWHCEVWTKPI 1WVDQWPF 5CNGU CPF %WUVQOGT 299
.QIKUVKEU .QIKUVKEU /CTMGVKPI 5GTXKEG
2WTEJCUG $KE[ENG 2CTVU
Customer Demand
Vendor
Database Vendor Query Query Finished
Goods
Vendor Database
Name
Update with
Finished Bicycle
Raw
Raw Materials Order Parts Query Materials Update with
Cash Database Shipped Bicycles
Bicycle
Update with Update with Query
CRM
Parts Received Parts Used Database
Raw Materials
Vendor Finished Goods Sales
Inventory Prospects
Components Customer
Receiving Finished Sales Pitch
Bicycle Customer Order
Accepted
Materials Make Bicycle Bicycles Cash
Approved Salesperson
Production Order
Schedule
Raw Materials Shipping Boxed Bicycles
Inventory
Manufacturing
Plan
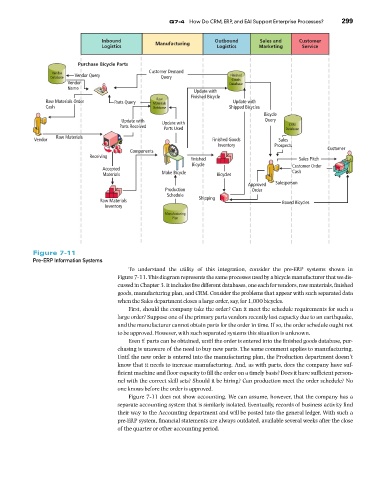
Figure 7-11
Pre-ERP Information Systems
To understand the utility of this integration, consider the pre-ERP systems shown in
Figure 7-11. This diagram represents the same processes used by a bicycle manufacturer that we dis-
cussed in Chapter 3. It includes five different databases, one each for vendors, raw materials, finished
goods, manufacturing plan, and CRM. Consider the problems that appear with such separated data
when the Sales department closes a large order, say, for 1,000 bicycles.
First, should the company take the order? Can it meet the schedule requirements for such a
large order? Suppose one of the primary parts vendors recently lost capacity due to an earthquake,
and the manufacturer cannot obtain parts for the order in time. If so, the order schedule ought not
to be approved. However, with such separated systems this situation is unknown.
Even if parts can be obtained, until the order is entered into the finished goods database, pur-
chasing is unaware of the need to buy new parts. The same comment applies to manufacturing.
Until the new order is entered into the manufacturing plan, the Production department doesn’t
know that it needs to increase manufacturing. And, as with parts, does the company have suf-
ficient machine and floor capacity to fill the order on a timely basis? Does it have sufficient person-
nel with the correct skill sets? Should it be hiring? Can production meet the order schedule? No
one knows before the order is approved.
Figure 7-11 does not show accounting. We can assume, however, that the company has a
separate accounting system that is similarly isolated. Eventually, records of business activity find
their way to the Accounting department and will be posted into the general ledger. With such a
pre-ERP system, financial statements are always outdated, available several weeks after the close
of the quarter or other accounting period.