Page 218 - Valve Selection Handbook
P. 218
Pressure Relief Valves 205
system fluid and therefore do not suffer thermal shock on valve opening.
Second, solids carried by the discharging fluid do not impact directly on
the seating surface of the piston. Location of the piston within the pres-
sure zone therefore significantly reduces potential seating damage. The
opening and closing deceleration of the piston is controlled in this case
by built-in dampers to limit mechanical shock on valve and piping sys-
tem on valve opening and closing.
Standard and full-bore flanged steel main valves. API Standard 526,
which covers end connections, nozzle sizes, and pressure and tempera-
ture limits of flanged steel spring-loaded pressure relief valves, has been
extended to cover pilot-operated valves as well as spring-loaded pressure
relief valves.
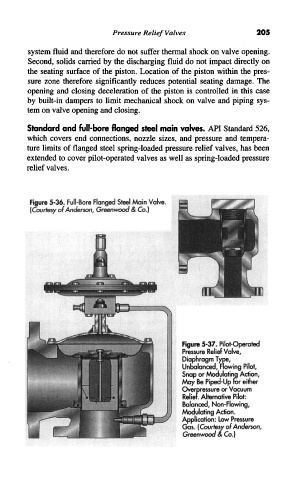
Figure 5-36. Full-Bore Flanged Steel Main Valve.
(Courtesy of Anderson, Greenwood & Co.)
Figure 5-37. Pilot-Operated
Pressure Relief Valve,
Diaphragm Type,
Unbalanced, Flowing Pilot,
Snap or Modulating Action,
May Be Piped-Up for either
Overpressure or Vacuum
Relief. Alternative Pilot:
Balanced, Non-Flowing,
Modulating Action.
Application: Low Pressure
Gas. (Courtesy of Anderson,
Greenwood & Co.)