Page 253 - Valve Selection Handbook
P. 253
240 Valve Selection Handbook
The graphite commonly used for the manufacture of rupture discs is
the resin-impregnated grade. The material is very brittle and ruptures
almost without deformation. Its structure is very homogeneous and the
strength of the material is low compared with the strength of metals.
Graphite rupture discs are therefore much thicker than metal rupture
discs. This property permits graphite rupture discs to be made to small
burst pressure tolerances.
Pure graphite is a flexible material that is used for the manufacture of
reverse-buckling discs. Because pure graphite is free of resin impregna-
tion, pure graphite rupture discs may be exposed to higher operating tem-
peratures.
Graphite rupture discs may be used in both gas and liquid-full services.
Monoblock-type graphite rupture discs. Rupture discs made of resin-
impregnated graphite are commonly produced in monoblock form, as
shown in Figure 6-24 through Figure 6-26. These are one-piece devices
that combine a flat bursting membrane with the mounting flange.
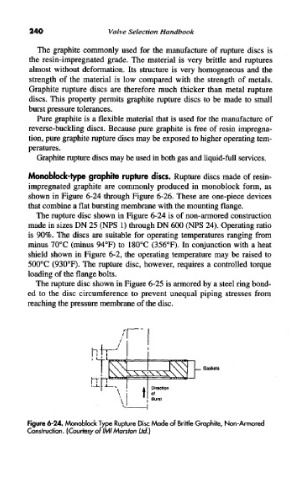
The rupture disc shown in Figure 6-24 is of non-armored construction
made in sizes DN 25 (NFS 1) through DN 600 (NFS 24). Operating ratio
is 90%. The discs are suitable for operating temperatures ranging from
minus 70°C (minus 94°F) to 180°C (356°F). In conjunction with a heat
shield shown in Figure 6-2, the operating temperature may be raised to
500°C (930°F). The rupture disc, however, requires a controlled torque
loading of the flange bolts.
The rupture disc shown in Figure 6-25 is armored by a steel ring bond-
ed to the disc circumference to prevent unequal piping stresses from
reaching the pressure membrane of the disc.
Figure 6-24. Monoblock Type Rupture Disc Made of Brittle Graphite, Non-Armored
Construction. (Courtesy oflMI Mars/on Ltd.)