Page 237 - Video Coding for Mobile Communications Efficiency, Complexity, and Resilience
P. 237
214 Chapter 9. Error-Resilience Video Coding Techniques
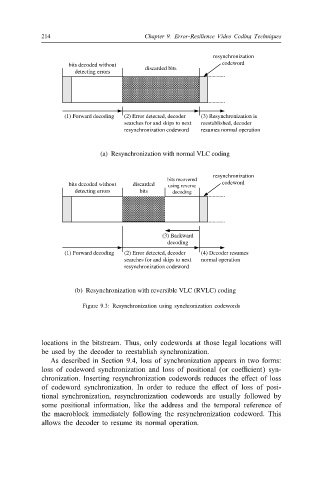
resynchronization
bits decoded without discarded bits codeword
detecting errors
(1) Forward decoding (2) Error detected, decoder (3) Resynchronization is
searches for and skips to next reestablished, decoder
resynchronization codeword resumes normal operation
(a) Resynchronization with normal VLC coding
resynchronization
bits recovered
bits decoded without discarded using reverse codeword
detecting errors bits decoding
(3) Backward
decoding
(1) Forward decoding (2) Error detected, decoder (4) Decoder resumes
searches for and skips to next normal operation
resynchronization codeword
(b) Resynchronization with reversible VLC (RVLC) coding
Figure 9.3: Resynchronization using synchronization codewords
locations in the bitstream. Thus, only codewords at those legal locations will
be used by the decoder to reestablish synchronization.
As described in Section 9.4, loss of synchronization appears in two forms:
loss of codeword synchronization and loss of positional (or coe$cient) syn-
chronization. Inserting resynchronization codewords reduces the e ect of loss
of codeword synchronization. In order to reduce the e ect of loss of posi-
tional synchronization, resynchronization codewords are usually followed by
some positional information, like the address and the temporal reference of
the macroblock immediately following the resynchronization codeword. This
allows the decoder to resume its normal operation.