Page 85 - Vogel's TEXTBOOK OF QUANTITATIVE CHEMICAL ANALYSIS
P. 85
COMPLEXONES 2.26
HA
/\
(CH,), CH,COOH (CH,), CH,COOH
\ \+ ,CH,COO-
HN
/
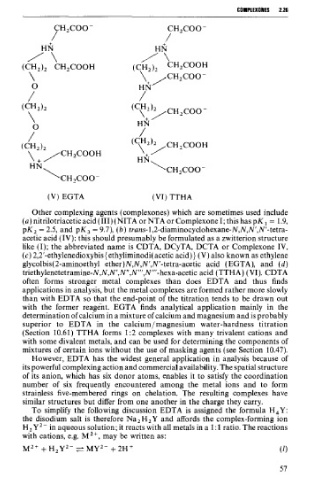
(V) EGTA (VI) TTHA
Other complexing agents (complexones) which are sometimes used include
(a) nitrilotriacetic acid (III) (NITA or NTA or Complexone 1; this has pK, = 1.9,
pK, = 2.5, and pK, = 9.7), (b) trans-l,2-diaminocyclohexane-N,N,N1,N'-tetra-
acetic acid (IV): this should presumably be formulated as a zwitterion structure
like (1); the abbreviated name is CDTA, DCyTA, DCTA or Complexone IV,
(c) 2,2'-ethylenedioxybis {ethyliminodi(acetic acid)) (V) also known as ethylene
glycolbis(2-aminoethyl ether)N,N,N1,N'-tetra-acetic acid (EGTA), and (d)
triethylenetetramine-N,N,N',N",N"',N"'-hexa-acetic acid (TTHA) (VI). CDTA
often forms stronger metal complexes than does EDTA and thus finds
applications in analysis, but the metal complexes are formed rather more slowly
than with EDTA so that the end-point of the titration tends to be drawn out
with the former reagënt. EGTA finds analytical application mainly in the
determination of calcium in a mixture of calcium and magnesium and is probably
superior to EDTA in the calcium/magnesium water-hardness titration
(Section 10.61) TTHA forms 1:2 complexes with many trivalent cations and
with some divalent metals, and can be used for determining the components of
mixtures of certain ions without the use of masking agents (see Section 10.47).
However, EDTA has the widest general application in analysis because of
its powerful complexing action and commercial availability. The spatial structure
of its anion, which has six donor atoms, enables it to satisfy the coordination
number of six frequently encountered among the metal ions and to form
strainless five-membered rings on chelation. The resulting complexes have
similar structures but differ from one another in the charge they carry.
To simplify the following discussion EDTA is assigned the formula H,Y:
the disodium Salt is therefore Na,H,Y and affords the complex-forming ion
H2YZ- in aqueous solution; it reacts with al1 metals in a 1 : 1 ratio. The reactions
with cations, e.g. M2+, may be written as: