Page 216 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 216
CAT3525_C07.qxd 1/29/2005 9:57 AM Page 187
Municipal Solid Waste Processing; Materials Recovery Facilities 187
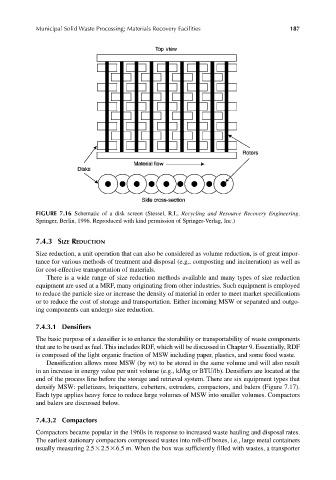
FIGURE 7.16 Schematic of a disk screen (Stessel, R.I., Recycling and Resource Recovery Engineering.
Springer, Berlin, 1996. Reproduced with kind permission of Springer-Verlag, Inc.)
7.4.3 SIZE REDUCTION
Size reduction, a unit operation that can also be considered as volume reduction, is of great impor-
tance for various methods of treatment and disposal (e.g., composting and incineration) as well as
for cost-effective transportation of materials.
There is a wide range of size reduction methods available and many types of size reduction
equipment are used at a MRF, many originating from other industries. Such equipment is employed
to reduce the particle size or increase the density of material in order to meet market specifications
or to reduce the cost of storage and transportation. Either incoming MSW or separated and outgo-
ing components can undergo size reduction.
7.4.3.1 Densifiers
The basic purpose of a densifier is to enhance the storability or transportability of waste components
that are to be used as fuel. This includes RDF, which will be discussed in Chapter 9. Essentially, RDF
is composed of the light organic fraction of MSW including paper, plastics, and some food waste.
Densification allows more MSW (by wt) to be stored in the same volume and will also result
in an increase in energy value per unit volume (e.g., kJ/kg or BTU/lb). Densifiers are located at the
end of the process line before the storage and retrieval system. There are six equipment types that
densify MSW: pelletizers, briquetters, cubetters, extruders, compactors, and balers (Figure 7.17).
Each type applies heavy force to reduce large volumes of MSW into smaller volumes. Compactors
and balers are discussed below.
7.4.3.2 Compactors
Compactors became popular in the 1960s in response to increased waste hauling and disposal rates.
The earliest stationary compactors compressed wastes into roll-off boxes, i.e., large metal containers
usually measuring 2.5 2.5 6.5 m. When the box was sufficiently filled with wastes, a transporter