Page 592 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 592
CAT3525_C19.qxd 1/28/2005 5:05 PM Page 563
Management of Used Oil 563
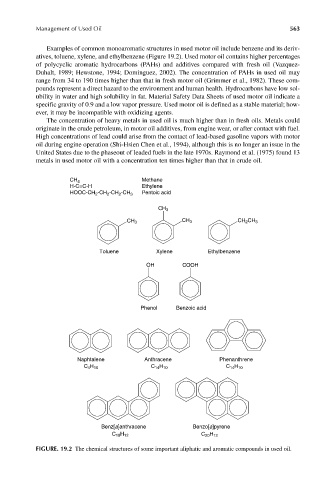
Examples of common monoaromatic structures in used motor oil include benzene and its deriv-
atives, toluene, xylene, and ethylbenzene (Figure 19.2). Used motor oil contains higher percentages
of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and additives compared with fresh oil (Vazquez-
Duhalt, 1989; Hewstone, 1994; Dominguez, 2002). The concentration of PAHs in used oil may
range from 34 to 190 times higher than that in fresh motor oil (Grimmer et al., 1982). These com-
pounds represent a direct hazard to the environment and human health. Hydrocarbons have low sol-
ubility in water and high solubility in fat. Material Safety Data Sheets of used motor oil indicate a
specific gravity of 0.9 and a low vapor pressure. Used motor oil is defined as a stable material; how-
ever, it may be incompatible with oxidizing agents.
The concentration of heavy metals in used oil is much higher than in fresh oils. Metals could
originate in the crude petroleum, in motor oil additives, from engine wear, or after contact with fuel.
High concentrations of lead could arise from the contact of lead-based gasoline vapors with motor
oil during engine operation (Shi-Hsien Chen et al., 1994), although this is no longer an issue in the
United States due to the phaseout of leaded fuels in the late 1970s. Raymond et al. (1975) found 13
metals in used motor oil with a concentration ten times higher than that in crude oil.
CH 4 Methane
H-C=C-H Ethylene
HOOC-CH -CH -CH -CH 3 Pentoic acid
2
2
2
CH 3
CH 3 CH 3 CH 2 CH 3
Toluene Xylene Ethylbenzene
OH COOH
Phenol Benzoic acid
Naphtalene Anthracene Phenanthrene
C 4 H 10 C 14 H 10 C 14 H 10
Benz[a]anthracene Benzo[a]pyrene
C 18 H 12 C 20 H 12
FIGURE. 19.2 The chemical structures of some important aliphatic and aromatic compounds in used oil.