Page 631 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 631
CAT3525_C20.qxd 1/27/2005 12:54 PM Page 602
602 Waste Management Practices: Municipal, Hazardous, and Industrial
waste to a small particle size, thereby increasing particle surface area which increases contact with
the chemical agent and ultimately sterilizes the waste. Disinfectants (antimicrobial agents) may be
used alone or in combination with encapsulating agents.
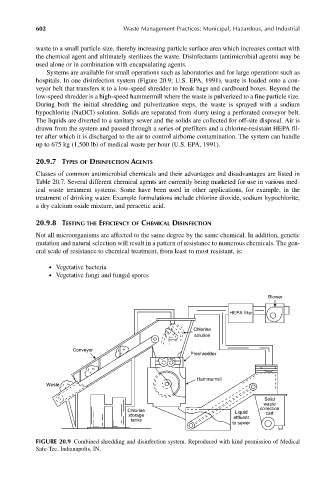
Systems are available for small operations such as laboratories and for large operations such as
hospitals. In one disinfection system (Figure 20.9; U.S. EPA, 1991), waste is loaded onto a con-
veyor belt that transfers it to a low-speed shredder to break bags and cardboard boxes. Beyond the
low-speed shredder is a high-speed hammermill where the waste is pulverized to a fine particle size.
During both the initial shredding and pulverization steps, the waste is sprayed with a sodium
hypochlorite (NaOCl) solution. Solids are separated from slurry using a perforated conveyor belt.
The liquids are diverted to a sanitary sewer and the solids are collected for off-site disposal. Air is
drawn from the system and passed through a series of prefilters and a chlorine-resistant HEPA fil-
ter after which it is discharged to the air to control airborne contamination. The system can handle
up to 675 kg (1,500 lb) of medical waste per hour (U.S. EPA, 1991).
20.9.7 TYPES OF DISINFECTION AGENTS
Classes of common antimicrobial chemicals and their advantages and disadvantages are listed in
Table 20.7. Several different chemical agents are currently being marketed for use in various med-
ical waste treatment systems. Some have been used in other applications, for example, in the
treatment of drinking water. Example formulations include chlorine dioxide, sodium hypochlorite,
a dry calcium oxide mixture, and peracetic acid.
20.9.8 TESTING THE EFFICIENCY OF CHEMICAL DISINFECTION
Not all microorganisms are affected to the same degree by the same chemical. In addition, genetic
mutation and natural selection will result in a pattern of resistance to numerous chemicals. The gen-
eral scale of resistance to chemical treatment, from least to most resistant, is:
● Vegetative bacteria
● Vegetative fungi and fungal spores
Blower
HEPA filter
Chlorine
solution
Conveyor
Preshredder
Hammermill
Waste
Solid
waste
collection
Chlorine Liquid
storage cart
tanks effluent
to sewer
FIGURE 20.9 Combined shredding and disinfection system. Reproduced with kind permission of Medical
Safe-Tec, Indianapolis, IN.