Page 120 - Wastewater Solids Incineration Systems
P. 120
Combustion Technology 89
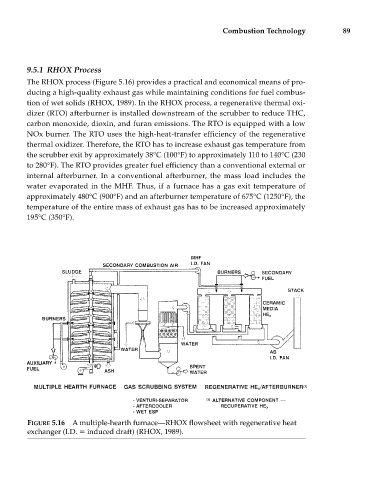
9.5.1 RHOX Process
The RHOX process (Figure 5.16) provides a practical and economical means of pro-
ducing a high-quality exhaust gas while maintaining conditions for fuel combus-
tion of wet solids (RHOX, 1989). In the RHOX process, a regenerative thermal oxi-
dizer (RTO) afterburner is installed downstream of the scrubber to reduce THC,
carbon monoxide, dioxin, and furan emissions. The RTO is equipped with a low
NOx burner. The RTO uses the high-heat-transfer efficiency of the regenerative
thermal oxidizer. Therefore, the RTO has to increase exhaust gas temperature from
the scrubber exit by approximately 38°C (100°F) to approximately 110 to 140°C (230
to 280°F). The RTO provides greater fuel efficiency than a conventional external or
internal afterburner. In a conventional afterburner, the mass load includes the
water evaporated in the MHF. Thus, if a furnace has a gas exit temperature of
approximately 480°C (900°F) and an afterburner temperature of 675°C (1250°F), the
temperature of the entire mass of exhaust gas has to be increased approximately
195°C (350°F).
FIGURE 5.16 A multiple-hearth furnace—RHOX flowsheet with regenerative heat
exchanger (I.D. induced draft) (RHOX, 1989).