Page 274 - Water Engineering Hydraulics, Distribution and Treatment
P. 274
252
Pumping, Storage, and Dual Water Systems
Chapter 8
Useful
storage
Useful
storage
storage
Supporting
storage Supporting
Inlet and Inlet and Drain
Overflow outlet outlet
Drain
(a) (b)
Useful
storage
Municipal
offices, etc.
Original surface
Inlet and Drain
outlet
(c) (d)
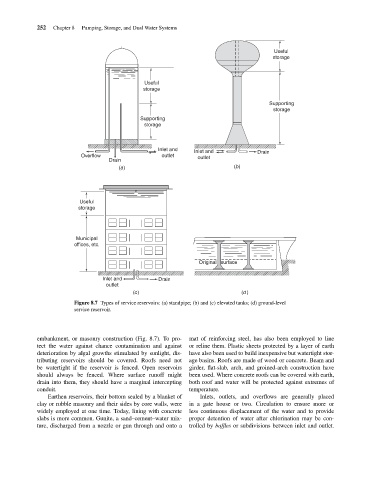
Figure 8.7 Types of service reservoirs: (a) standpipe; (b) and (c) elevated tanks; (d) ground-level
service reservoir.
embankment, or masonry construction (Fig. 8.7). To pro- mat of reinforcing steel, has also been employed to line
tect the water against chance contamination and against or reline them. Plastic sheets protected by a layer of earth
deterioration by algal growths stimulated by sunlight, dis- have also been used to build inexpensive but watertight stor-
tributing reservoirs should be covered. Roofs need not age basins. Roofs are made of wood or concrete. Beam and
be watertight if the reservoir is fenced. Open reservoirs girder, flat-slab, arch, and groined-arch construction have
should always be fenced. Where surface runoff might been used. Where concrete roofs can be covered with earth,
drain into them, they should have a marginal intercepting both roof and water will be protected against extremes of
conduit. temperature.
Earthen reservoirs, their bottom sealed by a blanket of Inlets, outlets, and overflows are generally placed
clay or rubble masonry and their sides by core walls, were in a gate house or two. Circulation to ensure more or
widely employed at one time. Today, lining with concrete less continuous displacement of the water and to provide
slabs is more common. Gunite, a sand–cement–water mix- proper detention of water after chlorination may be con-
ture, discharged from a nozzle or gun through and onto a trolled by baffles or subdivisions between inlet and outlet.