Page 239 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 239
6-16 WATER AND WASTEWATER ENGINEERING
the specifics of the product. Dry and liquid forms are available. The properties of iron with respect
to forming large complexes, dose, and pH curves are similar to those of alum. An example of the
reaction of FeCl 3 in the presence of alkalinity is
FeCl 3 HCO 3 H O FeOH
( ) 3 3 H O s ( ) 3 CO 3 Cll (6-10)
2
3
2
2
3
and without alkalinity
3 H O ( )
3 H O s ( ) 3 HCl (6-11)
FeCl 3 2 FeOH 3 2
forming hydrochloric acid, which in turn lowers the pH.
pH and Dose
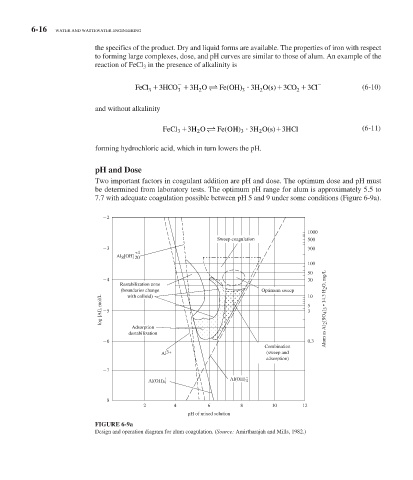
Two important factors in coagulant addition are pH and dose. The optimum dose and pH must
be determined from laboratory tests. The optimum pH range for alum is approximately 5.5 to
7.7 with adequate coagulation possible between pH 5 and 9 under some conditions ( Figure 6-9 a).
2
1000
Sweep coagulation 500
3 300
4
Al 8 [OH] 20
100
50
4 30
Restabilization zone
(boundaries change Optimum sweep 10
with colloid)
log [Al], mol/L 5 5 3 Alum as Al 2 [SO 4 ] 3 • 14.3 H 2 O, mg/L
Adsorption
destabilization
6 0.3
Combination
Al 3 (sweep and
adsorption)
7
Al(OH) 4 Al(OH) 4
8
2 4 6 8 10 12
pH of mixed solution
FIGURE 6-9a
Design and operation diagram for alum coagulation. (Source: Amirtharajah and Mills, 1982.)