Page 294 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 294
LIME–SODA SOFTENING 7-11
0
CaCO (s)
3
–2
–4
log[Ca 2+ ] C =10 –4
T
–6
C =10 –2
T
–8
C =10 0
T
–10
2 4 6 8 10 12 14
pH
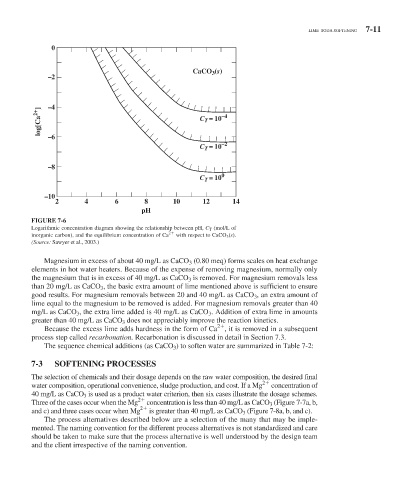
FIGURE 7-6
Logarithmic concentration diagram showing the relationship between pH, C T (mol/L of
inorganic carbon), and the equilibrium concentration of Ca 2 with respect to CaCO 3 (s).
(Source: Sawyer et al., 2003.)
Magnesium in excess of about 40 mg/L as CaCO 3 (0.80 meq) forms scales on heat exchange
elements in hot water heaters. Because of the expense of removing magnesium, normally only
the magnesium that is in excess of 40 mg/L as CaCO 3 is removed. For magnesium removals less
than 20 mg/L as CaCO 3 , the basic extra amount of lime mentioned above is sufficient to ensure
good results. For magnesium removals between 20 and 40 mg/L as CaCO 3 , an extra amount of
lime equal to the magnesium to be removed is added. For magnesium removals greater than 40
mg/L as CaCO 3 , the extra lime added is 40 mg/L as CaCO 3 . Addition of extra lime in amounts
greater than 40 mg/L as CaCO 3 does not appreciably improve the reaction kinetics.
2
Because the excess lime adds hardness in the form of Ca , it is removed in a subsequent
process step called recarbonation. Recarbonation is discussed in detail in Section 7.3.
The sequence chemical additions (as CaCO 3 ) to soften water are summarized in Table 7-2 :
7-3 SOFTENING PROCESSES
The selection of chemicals and their dosage depends on the raw water composition, the desired final
2
water composition, operational convenience, sludge production, and cost. If a Mg concentration of
40 mg/L as CaCO 3 is used as a product water criterion, then six cases illustrate the dosage schemes.
2
Three of the cases occur when the Mg concentration is less than 40 mg/L as CaCO 3 ( Figure 7-7a , b,
2
and c) and three cases occur when Mg is greater than 40 mg/L as CaCO 3 ( Figure 7-8a , b, and c).
The process alternatives described below are a selection of the many that may be imple-
mented. The naming convention for the different process alternatives is not standardized and care
should be taken to make sure that the process alternative is well understood by the design team
and the client irrespective of the naming convention.