Page 295 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 295
7-12 WATER AND WASTEWATER ENGINEERING
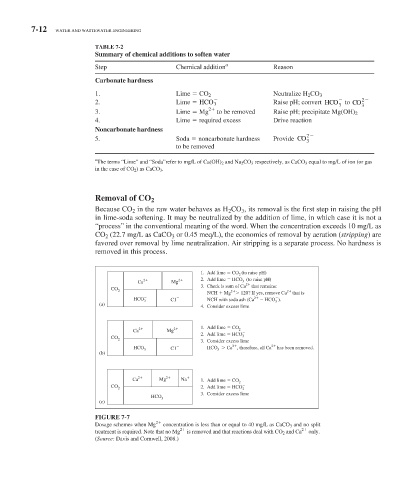
TABLE 7-2
Summary of chemical additions to soften water
a
Step Chemical addition Reason
Carbonate hardness
1. Lime CO 2 Neutralize H 2 CO 3
2
2. Raise pH; convert HCO to CO
Lime HCO 3
3 3
2
3. Lime Mg to be removed Raise pH; precipitate Mg(OH) 2
4. Lime required excess Drive reaction
Noncarbonate hardness
2
5. Soda noncarbonate hardness Provide CO 3
to be removed
a
The terms “Lime” and “Soda”refer to mg/L of Ca(OH) 2 and Na 2 CO 3 respectively, as CaCO 3 equal to mg/L of ion (or gas
in the case of CO 2 ) as CaCO 3 .
Removal of CO 2
Because CO 2 in the raw water behaves as H 2 CO 3 , its removal is the first step in raising the pH
in lime-soda softening. It may be neutralized by the addition of lime, in which case it is not a
“process” in the conventional meaning of the word. When the concentration exceeds 10 mg/L as
CO 2 (22.7 mg/L as CaCO 3 or 0.45 meq/L), the economics of removal by aeration ( stripping ) are
favored over removal by lime neutralization. Air stripping is a separate process. No hardness is
removed in this process.
1. Add lime CO (to raise pH)
2
3
Ca 2 Mg 2 2. Add lime HCO (to raise pH)
3. Check is sum of Ca 2 that remains:
CO
2 2 2
NCH Mg 120? If yes, remove Ca that is
HCO 3 C1 NCH with soda ash (Ca 2 HCO ).
(a) 3
4. Consider excess lime
2 2 1. Add lime CO 2
Ca Mg
2. Add lime HCO
CO 3
2
3. Consider excess lime
2
HCO 3 C1 HCO Ca , therefore, all Ca 2 has been removed.
3
(b)
Ca 2 Mg 2 Na
1. Add lime CO 2
CO 2. Add lime HCO
2 3
HCO 3. Consider excess lime
3
(c)
FIGURE 7-7
2
Dosage schemes when Mg concentration is less than or equal to 40 mg/L as CaCO 3 and no split
2 2
treatment is required. Note that no Mg is removed and that reactions deal with CO 2 and Ca only.
(Source: Davis and Cornwell, 2008.)