Page 114 - Welding Robots Technology, System Issues, and Applications
P. 114
100 Welding Robots
x
x A minimum mass transferred per short-circuit
A minimum spatter loss
A deviation from the optimal welding conditions is assumed to lead to a higher
probability of spatter, uneven weld-bead and other fusion effects. To detect this, it
is shown that monitoring of the weld voltage and using the variance of the voltage
is a robust feature. Other features could also be used like short-circuiting rate and
arc time, but they are less robust to detect defective welds.
80
Variance of weld
70
voltage
60
50
gap
40
30
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
400
300 Decision
Alarm function
threshold
200
100
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
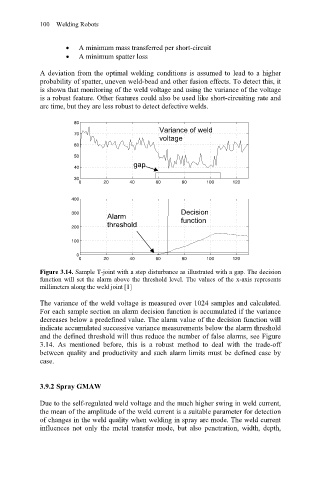
Figure 3.14. Sample T-joint with a step disturbance as illustrated with a gap. The decision
function will set the alarm above the threshold level. The values of the x-axis represents
millimeters along the weld joint [1]
The variance of the weld voltage is measured over 1024 samples and calculated.
For each sample section an alarm decision function is accumulated if the variance
decreases below a predefined value. The alarm value of the decision function will
indicate accumulated successive variance measurements below the alarm threshold
and the defined threshold will thus reduce the number of false alarms, see Figure
3.14. As mentioned before, this is a robust method to deal with the trade-off
between quality and productivity and such alarm limits must be defined case by
case.
3.9.2 Spray GMAW
Due to the self-regulated weld voltage and the much higher swing in weld current,
the mean of the amplitude of the weld current is a suitable parameter for detection
of changes in the weld quality when welding in spray arc mode. The weld current
influences not only the metal transfer mode, but also penetration, width, depth,