Page 176 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 176
°
159
mechanisms (brittle
base-
a
rifts
associated
more
;
and
and Range
processe
of
formation
complexity
continent
crystalline
is
Settings
crust
be
th ose
Basin
to
crust;
Asa
lower
Tectonic
structural
the
thought
of
the
lower
different
The
that
combination
Crust
Zone
from
of
events,
reveal
6.24a).
to
the
Expression
Reflective Lower
profiles
due
of
through
2.15)
transparent,
underplating
discontinuous
(Fig.
a
Rift
Seismic
Reflection
1987).
to
(Fig.
contrasts
but
or
thin,
States
al.,
extension, H
Crust;
commonly
Continental
and
et
short,
crusts
impedance
respectively).
Potter
United
extension
Upper
exhibiting
lower
1987;
ductile
is
western
Nonreflective
crust
acoustic
ductile
and
al.,
failure,
upper
(6.24b),
magmatism, :
et
upper
the
(Allmendinger
faults;
large
of
and ductile
the
Moho.
4
the
2.
reflective
Province
of
1,
of
normal
apart,
ment
new
with
lack
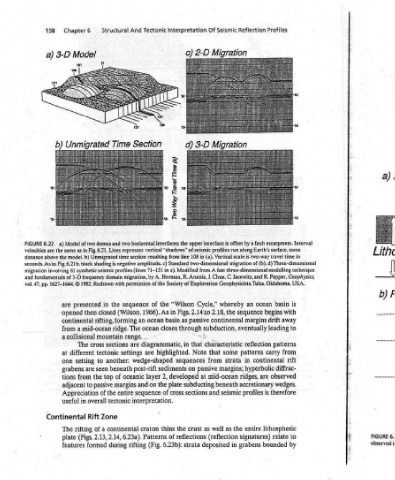
a) Cross Lithosphere Section SS ££ 50-500kmn Nonreflective stent “1, (brittle) crust. upper Reflective 2. (ductile) crust. lower Horizontal 3. reflections. Moho Wedge-shaped 4. sequences filling rift grabens. Occasional 5. fault-zone reflections. sl se eer le! p! ismi zone. b) Seismic reflection i patterns commonly
aa
escarpment. Interval time in modelling technique is with away to patterns from rift diffrac- to by
Profiles along Earth’s surface, some migration of (b).d) Three-dimensional basin begins drift leading carry continental observed accretionary wedges. therefore is lithospheric relate bounded
Reflection fault by a scale is two-way travel three-dimensional Geophysicists, Tulsa, Oklahoma, USA. ocean an sequence margins eventually reflection patterns in hyperbolic are ridges, profiles entire signatures) grabens
Seismic Migration is offset fast whereby the subduction, characteristic some strata margins; mid-ocean seismic the as (reflection in
Of 2-D upper interface (a). Vertical two-dimensional from A Cycle,” 2.18, 2.14't0 passive continental NEA that from passive at subducting beneath and well as deposited
Interpretation c) (Ss) euny jeaesy AB OME interfaces; the vertical “shadows” of seismic profiles run 108 in line a), Modified fundamentals of 3-D frequency domain migration, by A. Herman, R. Anania, J. Chun, C. Jacewitz, and R. Pepper, Geophysics, Society of Exploration “Wilson Figs. in as basin through that in Note highlighted. sequences on sediments developed plate sections of cross
Tectonic resulting from amplitude. c) Standard in 71-131 permission of the the of 1966). As ocean closes ocean ... diagrammatic, are wedge-shaped post-rift 2, layer the on sequence interpretation. thins craton Patterns (Fig.
And two horizontal time section sequence (Wilson, an range. are settings oceanic and entire 6.23a). rifting
Structural n Eee Ne Se the same as in Fig. 6.21. Lines represent Unmigrated shading is negative synthetic seismic profiles (lines the in closed rifting, forming mid-ocean ridge. The mountain sections cross tectonic another: to beneath seen of top the margins to passive of the tectonic overall Zone continental a of 2.14, 2.13, during formed
Chapter6 Model 101 oe _— " Model of two domes and model. b) 1627-1644, © 1982. Redrawn with presented then opened continental a collisional The different setting are grabens from adjacent Appreciation in useful Rift rifting (Figs. features
3-D a) the seconds. As in Fig. 6.21b. black involving 61 are from a at one tions Continental The plate
158 a) 6.22
FIGURE velocities are distance above migration and vol. 47, pp.