Page 190 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 190
is
(d)
in
Rectangle
basin closure and continental collision.
Active Continental Margin
Flysch/Molasse
Thrusting
_-External Massif
;
Subduction
Margin
thick
in
Lithospheric cross sections illustrating stages of ocean
—
Basin
Passive
Involved
Foreland
Crust
During
Belt
Ocean
Fold-and-
~— Ocoganic
of
Thrust
Basement
Underthrusting
Closes
Décollement
Passive Continental Margin’
Fig. 6.36.
Basin
Continental
in
Ocean
region portrayed
Initial
6.35
FIGURE
c)
b)
a)
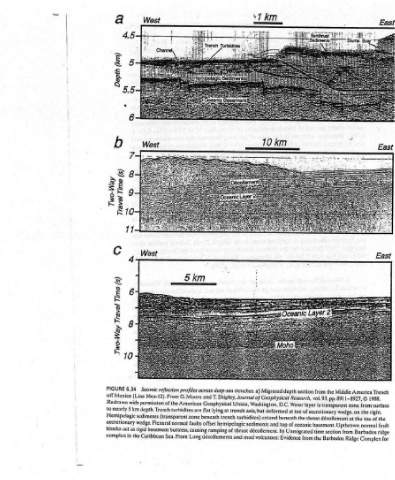
Middle America Trench wedge, by G. development of an accretionary the in pressure pore-fluid role of high the (continued) 6.34 FIGURE Geological Society of permission of the Redrawn with 1983. 1988. © 11, pp. 279-283, © vol. M. Smith, Geology, Westbrook and top of oceanic layer 2 extends from representing the pattern cue Hy
Sot Layer 22% = the from vol. 93, pp. 8911-8927, is i aa MimeGAuuet dé thrust 3 ses b: time section possasiGl tells Barbados the trom
eee Sari eae en ic Migrated depth section Water D.C. | Melsteat of toe at beneath the of oceanic top if Unmigrated b) Evidence
§ dg eet EN Ley ve vx? Seo 2; ONO axis, but deformed and volcanoes:
he ees Sa Sorts ERIN VERN = T. Shipley, Journal of Geophysical Research, Washington, Union, Xi trench idi turbidites) extend hemi pelagic sediments i i ramping of thrust décollement. mud
Jo 5 a Bee wie Paitig- Foe 17 — reflection profiles across deep-sea trenches. a) i oe he: Moore Geophysical American the lyi flat turbidites are ying at trench beneath z normal faults offset basement buttress, causin ig ; 2 i Long décollements and Sea, From
Oceanic
‘A
BEST
e
Deg)
tae
Nn © ® S ismric ae ms ssion of depth. Trench km Hemipelagic sediments (trans parent zone accretionary wedge. Flexural vec rigid as Caribbean the in
~ nearly 5 !
w (wy) yjdeq (S) ew] JEABLL (s) euny janes, AeAA-OML a i P blocks act : complex
Aepf-OML O FIGU SiMe aa to