Page 248 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 248
1
Bouguer correction
231
ee
it
Gravity Anomalies
applied to the free ai
in Fig. 8.7.
FIGURE 8.10
pre
“aes
are
lars
f
a
i
f
2
ft
é
Anomaly
. x . yA
‘Net
ra
Bouguer Anomaly
;
—
Air
ae Free
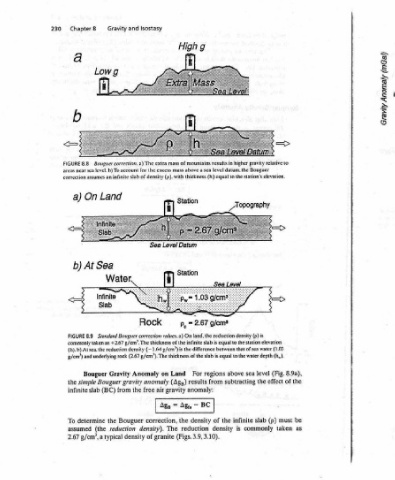
(fed) Apewouy AyAesy) Sar Stations os tg x Datum Level Sea Mass Deficiency correction Bouguer standard The thus: is level sea above areas for (0.0419)(2.67g/cm*)h = 0.0419ph BC = Xx h »Gal/m) (0.112 illustrates equation in m. The is h where eleva- surface of m 9 every about for that, increased the tion, adds point observation the below mass the to mGal 1 about observe
8.9a), (Fig. the of be must as taken
higher gravity relative to Bouguer Aopography of sea water (1.03 to the water depth (h,). level sea effect the (p) slab infinite commonly
results in mass of mountains datum. the level a sea thickness (h) equal to the station's elevation. ; Station Sea Lev 3 “al glem 2.67 = land, the reduction density (p) is On thickness of the infinite slab is equal to the station elevation between that g/cm’) is the difference thickness of the slab is equal above regions For subtracting from results anomaly: BC
Isostasy extra excess mass above for the slab of density (p). with Level Datum Sea fi] Station —p, Rock values.a) (2.67 g/cm’). The Land on Anomaly (Ag) anomaly gravity air free Ag; = Agp the correction, The density). (Figs. of granite
and Standard Bouguer correction +2.67 g/cm*. The the Bouguer density
Gravity Lowg Bouguer correction. a) The level. b) To account Land Sea Vee. Infinite sinh (h). b) At sea. the reduction density (— 1.64 Gravity Bouguer gravity from (BC) the reduction (the typical
Chapter8 a 8.8 FIGURE near sea areas correction assumes an infinite On a) ) At b) a 8.9 FIGURE commonly taken as g/cm’) and underlying rock Bouguer simple the slab infinite determine To assumed g/cm’, a 2.67