Page 267 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 267
ois the
249 maximum the is (the a by horizontal to estimate
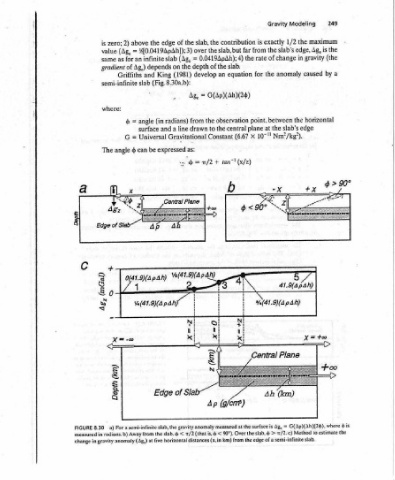
Modeling the 1/2 Ag, edge, gravity in caused the edge G(Ap)(Ah)(2$), where Method
Gravity exactly slab’s the of change anomaly the between the slab’s Nm?/kg?). ai err ¥4(41.9)(A pAh) = is Ag, «/2. ¢) b > the edge of a semi-infinite slab.
is from rate the for point, at plane 107!!! x SKE 9 <96° * the surface
contribution far slab, but 4) slab. equation G(Ap)(Ah)(26) observation central (6.67 tan™!(x/z) Phas at 90°). Over the slab, from km)
the the 0.0419ApAh); of the an the the to Constant + b < is,
slab, over = depth develop = from drawn 7/2 = (that
the (Ag, the Ag, Gravitational as: @/2 horizontal distances (x, in
of on (1981) 8.30a,b): . radians) line a -. Fora semi-infinite slab, the gravity anomaly measured <
edge 4(0.0419ApAh]); 3) slab King and expressed the slab,
the infinite depends and (Fig, , (in surface Universal be from five
above = an Ag,) slab angle = = can
2) (Ag, for as Griffiths G angle -00 = radians, b) Away in gravity anomaly (dg,) at
zero; value gradient of semi-infinite where: X (wy) yideq a)
is same The
8.30 in
FIGURE measured change
yideq
mass mas- the of buried the as approxi- as that (—Am) in: (or nega- thick- materials is (Ag,) (Fig. 8.9): rel- (Ag,) “too => the slab is
while more (lAg,!) is increases be gravity in 8.29a) deficit results increase or the of position contribution Slab of a
(+Ag,), the 2) amplitude sphere the can that changes slab (Fig. mass 8.29b) (Fig. an 2) ‘positive “s:) on .... surrounding attraction Bouguer correction to Ny S eteemrmmemimemed Ah)] mGal over edge = ye gees 0.0419(4 ph) inGal over slab field, depending on slab produces exactly a value directly over the slab’s
gravity (—Ag,); the as lAg;1) anomaly changes lateral infinite while slab slab; (3. the « is that to gravitational according the slab, Semi-Infinite ae *%&(0.0419(4p ne to the gravity mass anomaly. b) The gravity effect infinite
in decrease greater (smaller gravity model An (+Ag,), the from the 3) and from (Am) relative to the the +4m Ama Zero away from slab Bouguer correction. d) The gravity effect of semi-infinite (right), / of that
increase gravity the the of density to slabs. gravity Truncating far slab; but far (Ap) subtracts in used 0.0419(Ap)(Ah) however, changes from away b 1 CO! amount (—Am) is crossed. c) An
5
an a in larger:R), attenuated width are convenient infinite the regions the of slab anomaly or slab far e So 1 a
ag
3
g
causes results is the there is of increase (—Ag,). in edge the mass density adds infinite = 1) (+Am) or negative edge of the slab far out over the slab
Isostasy +Ap) and/or anomaly Earth; 4) Where it truncations decline effect the over a its slab the Ag, of a semi-infinite slab, 8.29d): (left).
and —Ap) Ap the the deeply. Slab layering, will to gravity crossing regions represents and the of that (Fig. Slab by 0.0419(4 pAh) mGal a) An infinite slab adds or subtracts a constant positive the for the the edge
Gravity implying implying (larger within more horizontal abrupt (+Am) gravity no gravity in effect slab (Ah) slab amount as - edge = -Ag~_ used slab Bouguer slab approximation
(+Am, (—Am, sphere anomaly; 3) deeply buried Semi-Infinite of mass the in gravity infinite the 8.29c). The same the effect slab’s the Infinite +Agz ~ ~ -Am N slab raises gravity represents a semi-infinite slab changes gradually as as the zero far away from
Chapter8 excess deficit the sive gravity more is sphere by mated effects the excess has will cause essentially 1) decrease) tive) An ness of (Fig. exactly gravity The to ative a +Am Cc 8.29 the slab gravity effect to the
9S
248 So + FIGURE whether same equal edge, and
(ep) 747