Page 265 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 265
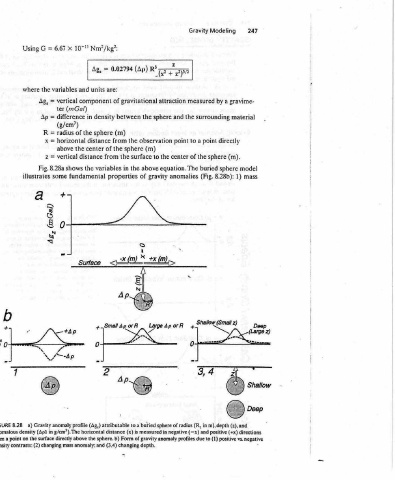
247 gravime- material mode] mass 1) (z), and (+x) directions >
Modeling a by surrounding directly (m). sphere sphere 8.28b): Shallow (Small z) a m), depth positive
Gravity Zz measured attraction the and point a to point the of center buried equation. The (Fig. anomalies ~ : + 0 in and of gravity anomaly profiles due to (1) positive vs. negative
Paap (Ap) of gravitational sphere the between observation the (m) sphere the to surface the above the in properties gravity of S 1 <X{m)_™ +x (m),, LargeAporR _ wx to a buried sphere of radius (R, (x) is measured in negative (—x) (3,4) changing depth.
Nm?/kg”: 0.02794 = Ag, are: units component density (m) sphere from distance the of center from variables SmallAporR 2 0 attributable (Ag,) distance horizontal the sphere. b) Form
107") and (121Gal) in the of the distance the fundamental Surtace
x vertical difference (g/em’) radius horizontal vertical shows —tA P
6.67 variables ter above 8.28a some + S Gravity anomaly profile in g/cm’). The
= = = Il Ul (opm) 737 on the surface directly above density contrasts; (2) changing mass anomaly: and
G the Ag, Ap R x z Fig. a (Ap
Using where illustrates a)
8.28 anomalous density point
b
FIGURE from a
Am
to compo- vertical attraction
due attraction and
point, vertical and of total gravitational
observation horizontal direction direction. horizontal of the to? 22)!” 22)! Zr
7R3) 1 r 1 2’) + (x? the at of and sphere of Ag of Ag Ag the sum (Ag,)? of + (x? = z + (x? 2”) Z ng (x?
(4/3 sum => Ag, + (Ag) the of component and vector + component (cos) z/r = SRG) r 1 +
G(Ap) 3 47R°G(Ap) 3 4nR°G(Ap) 3 attraction, vector > Ag, = magnitude mass —> Ag of =—> Ag component line the V(dg,)? Ag = = cos@ meaning (x? R°G(Ap)
= total a is — 2 of vertical as = vertica] Ag, 27, 4aR3G(Ap) 3 4.1888
isostesy Ag Ag = the attraction anomalous component component horizontal vertical a expressed Ag the Se(e/1) + x? 47/3: =
and of expressing the = = between be only = Se, = r = Ag, for Ag,
Gravity magnitude total vector to due is horizontal x vertical Ag(sin®) Ag(cos®) angle can measures value
the The (Fig. 8.27b): ut 8.27a: the
8 is 8.27a). —> Ag Ke, Re, Ag « = Ag, 8 magnitude gravimeter 8.27b): Fig. using:
Chapter that: so Ag (Fig. nents where: The com ponents: A (Fig. From that: so Again, Substituting
246