Page 316 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 316
299
Studies
Paleomagnetic
ect
0
oneubayy
1
°
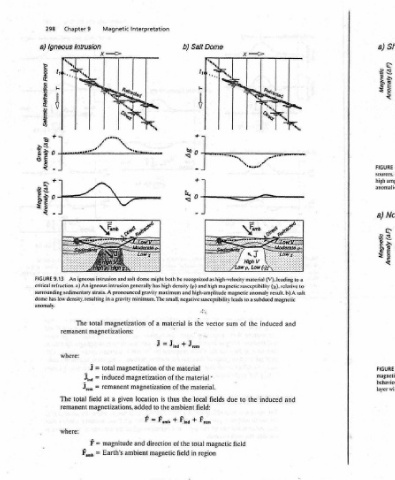
a) Basement Basement Magnetic Deep b) Magnetic Shallow ss + (Vv) Afewouy E Ve Surface Earth's surface depend on Magnetic anomalics measured at Depth to magnetic basement. 9.14 FIGURE of the magnetic depth the located sources. commonly anomalies, with rocks are shallow, short-wavelength basemeni basement. a) Where crystalline within results sedimentary cover beneath deeply bu
oneubey
salt
to
(V). leading to a (x). relative y magnetic susceptib result. b) A magnetic anomaly magnetic subdued leads to a and induced the of sum and induced the to due field
Salt Dome ‘a %, “ tre recognized as high-velocity material high and high-amplitude susceptibility o vector the material - material. fields local field: From magnetic total region
b) density (p) and small, negative is material the the ambient + Fina the in field
be the of + of
both high gravity maximum material of the of thus is the Foun magnetic
Interpretation s 9 § might dome gencrally has a gravity minimum. The a of magnetization magnetization magnetization location added to = F direction and ambient
Magnetic # igneous intrusion and salt intrusion A pronounced magnetization magnetizations: total induced Femanent given a at magnetizations, magnitude Earth’s
9 Intrusion x . x ‘ : igneous low density. resulting in total The = J j ind = J rem field fae Wout = em ‘amb
Chapter 7 An refraction. a) An surrounding sedimentary strata. remanent where: total The remanent where:
298 Igneous + f ° + f Ss 9.13 has
a) PIODOL UORIBYOL IILUSIOS (6y) Aswouy (49) Aewouy FIGURE critical dome anomaly.
AYABID oneubeyy