Page 39 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 39
21 Cookie is more and continents, associ- plate of underlying, are is pro- completely lithospheric a forms mar- “passive
Boundaries Oreo 150 and Oreo” cookie. lithosphere; oceanic the crust and asthenosphere convergent are a of interior movement the mantle. that regions lithosphere the that forces continents, at basin ocean the from termed
Plate between about divergent, (mountains, metamorphism) the by deeper thins, so elevated whether tensional continent different the large far ridge, are
of filling of an top part of the boundary between broad zone of increasing strength. in caused the 2.13). The a If of between a margins
Types Crust mantle lithosphere and boundaries: structures volcanism, boundaries, be to within lithosphere (Fig. on by 2.14a). parts as created enough, mid-ocean such
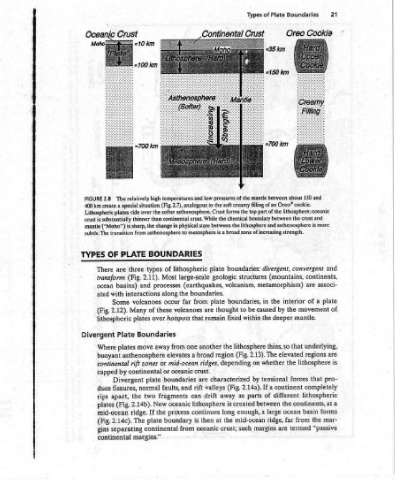
Continental temperatures and low pressures of the the soft creamy (Fig. 2.7), analogous to forms the the chemical the between is a mesosphere plate lithospheric geologic large-scale (earthquakes, boundaries. plate from far thought are volcanoes fixed remain that the another one region broad a depending ridges, crust. characterized are (Fig. valleys rift and away
#700 km high relatively situation over the softer asthenosphere. Crust ride thinner than continental crust. While is sharp, the change in physical state to asthenosphere from BOUNDARIES of types three Most 2.11). (Fig. processes and the along interactions occur volcanoes these of Many hotspots over plates Boundaries from away move elevates asthenosphere mid-ocean
The a special plates transition PLATE are basins) with Some 2.12). Plate plates by Divergent fissures, apart, (Fig. 2.14b). 2.14c). separating
2.8 400 km create crust is substantially mantle (“Moho”) OF There transform ocean ated (Fig. lithospheric Where buoyant continental capped duce rips plates mid-ocean (Fig. gins continental
FIGURE Lithospheric subtle. The TYPES Divergent
it fin- for pro- the apart, plates the first push
(eqW) eunsselg = g because our results enough years, within lithosphere. extends mid-ocean (subduction within the may oceanic which
g 10,000 15,000 8 as either Dashed also that cm/yr of plates at to basaltic eclogite,
viewed scale can be variables (Fig. 2.6a). two (Fig. 2.66). Percentages from Physical Geology by Sons, Inc., New York. but small, is it time. small is It years, million a over rates strain how hundreds millions of ranges. mountain convection by currents they rise, form to cools plate one motion created lithosphere deep-sea at trenches den
g in 1 slow currents split new commonly of lithospheric changes ridges
PR 700 mantle). Vertical (Earth’s linear the between relationship depth temperature with for upper mantle melt. Modified partial the of John Wiley and not important because only geologic over distances taken Yet rate. same is It see to easy thus over can, ductilly ocean and basins driven be to thought convection Where magma the mantle; the
Tectonics sana Geothermal Gradient for peridotite of the in volume of liquid versus solid in permission is rate large the km. 10 behave to as extensive are plates 2.10). from mantle, rock also may ridge the on divergent plate slab
Plate Normal diagram or depth, because increase 1987, with moving about at of as (Fig. magma new where the into recycles lithosphere motion to rise acting from downgoing lithospheric
2 100} & S S S Phase 2.7 © another. This plates in grow displacement asthenosphere features Lithospheric mantle converge constantly and Plate giving gravity away the on the
Chapter § (wy) yideq 600}. FIGURE Pressure line shows normal refer to the Skinner/Porter, one results gernails a in the duce upper generating Plates downward thus ridges zones). plates, idea, plates crust pulls
S
S
+
6)
20