Page 305 - Fluid Power Engineering
P. 305
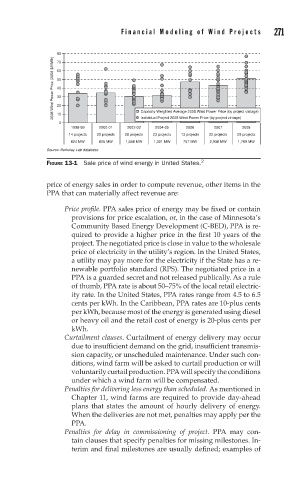
Financial Modeling of W ind Projects 271
80
2008 Wind Power Price (2008 $/MWh) 60
70
50
40
30
20
10
Individual Project 2008 Wind Power Price (by project vintage)
0 Capacity-Weighted Average 2008 Wind Power Price (by project vintage)
1998-99 2000-01 2002-03 2004-05 2006 2007 2008
14 projects 20 projects 28 projects 23 projects 13 projects 22 projects 25 projects
624 MW 805 MW 1,648 MW 1,331 MW 757 MW 2,938 MW 1,769 MW
Source: Berkeley Lab database
FIGURE 13-1 Sale price of wind energy in United States. 2
price of energy sales in order to compute revenue, other items in the
PPA that can materially affect revenue are:
Price profile. PPA sales price of energy may be fixed or contain
provisions for price escalation, or, in the case of Minnesota’s
Community Based Energy Development (C-BED), PPA is re-
quired to provide a higher price in the first 10 years of the
project. The negotiated price is close in value to the wholesale
price of electricity in the utility’s region. In the United States,
a utility may pay more for the electricity if the State has a re-
newable portfolio standard (RPS). The negotiated price in a
PPA is a guarded secret and not released publically. As a rule
of thumb, PPA rate is about 50–75% of the local retail electric-
ity rate. In the United States, PPA rates range from 4.5 to 6.5
cents per kWh. In the Caribbean, PPA rates are 10-plus cents
per kWh, because most of the energy is generated using diesel
or heavy oil and the retail cost of energy is 20-plus cents per
kWh.
Curtailment clauses. Curtailment of energy delivery may occur
due to insufficient demand on the grid, insufficient transmis-
sion capacity, or unscheduled maintenance. Under such con-
ditions, wind farm will be asked to curtail production or will
voluntarily curtail production. PPA will specify the conditions
under which a wind farm will be compensated.
Penalties for delivering less energy than scheduled. As mentioned in
Chapter 11, wind farms are required to provide day-ahead
plans that states the amount of hourly delivery of energy.
When the deliveries are not met, penalties may apply per the
PPA.
Penalties for delay in commissioning of project. PPA may con-
tain clauses that specify penalties for missing milestones. In-
terim and final milestones are usually defined; examples of