Page 33 - Fluid Power Engineering
P. 33
Basics of W ind Energy and Power 11
Sensitivity of Power to Rotor Radius and Wind Speed
The impact of change in radius by a small amount r, while all else
is constant, can be expressed as:
P/P = 2 r/r (2-6)
This means that if the radius is increased/decreased by 1%, power
will increase/decrease by 2%. For larger changes in radius, the above
formula does not apply; for instance, a 10% increase in radius will
lead to increase by 21% in power. A 20% increase in radius will lead
to 44% increase in power.
If speed is changed by a small amount and all else is constant, then
P/P = 3 v/v (2-7)
This means that if the speed is increased/decreased by 1%, energy will
increase/decrease by 3%. However, if the wind speed is increased by
20%, the power will increase by:
v 3
P 1 1 3
= 3 = (1.2) = 1.728 (2-8)
P 2 v
2
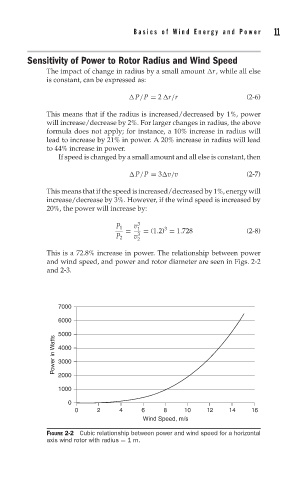
This is a 72.8% increase in power. The relationship between power
and wind speed, and power and rotor diameter are seen in Figs. 2-2
and 2-3.
7000
6000
5000
Power in Watts 4000
3000
2000
1000
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Wind Speed, m/s
FIGURE 2-2 Cubic relationship between power and wind speed for a horizontal
axis wind rotor with radius = 1m.