Page 236 - Wind Energy Handbook
P. 236
210 DESIGN LOADS FOR HORIZONTAL-AXIS WIND TURBINES
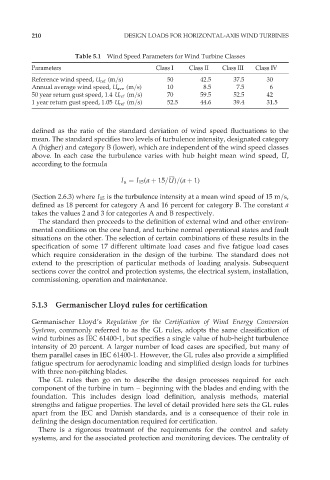
Table 5.1 Wind Speed Parameters for Wind Turbine Classes
Parameters Class I Class II Class III Class IV
Reference wind speed, U ref (m=s) 50 42.5 37.5 30
Annual average wind speed, U ave (m=s) 10 8.5 7.5 6
50 year return gust speed, 1:4 U ref (m=s) 70 59.5 52.5 42
1 year return gust speed, 1:05 U ref (m=s) 52.5 44.6 39.4 31.5
defined as the ratio of the standard deviation of wind speed fluctuations to the
mean. The standard specifies two levels of turbulence intensity, designated category
A (higher) and category B (lower), which are independent of the wind speed classes
above. In each case the turbulence varies with hub height mean wind speed, U,
according to the formula
I u ¼ I 15 (a þ 15=U)=(a þ 1)
(Section 2.6.3) where I 15 is the turbulence intensity at a mean wind speed of 15 m=s,
defined as 18 percent for category A and 16 percent for category B. The constant a
takes the values 2 and 3 for categories A and B respectively.
The standard then proceeds to the definition of external wind and other environ-
mental conditions on the one hand, and turbine normal operational states and fault
situations on the other. The selection of certain combinations of these results in the
specification of some 17 different ultimate load cases and five fatigue load cases
which require consideration in the design of the turbine. The standard does not
extend to the prescription of particular methods of loading analysis. Subsequent
sections cover the control and protection systems, the electrical system, installation,
commissioning, operation and maintenance.
5.1.3 Germanischer Lloyd rules for certification
Germanischer Lloyd’s Regulation for the Certification of Wind Energy Conversion
Systems, commonly referred to as the GL rules, adopts the same classification of
wind turbines as IEC 61400-1, but specifies a single value of hub-height turbulence
intensity of 20 percent. A larger number of load cases are specified, but many of
them parallel cases in IEC 61400-1. However, the GL rules also provide a simplified
fatigue spectrum for aerodynamic loading and simplified design loads for turbines
with three non-pitching blades.
The GL rules then go on to describe the design processes required for each
component of the turbine in turn – beginning with the blades and ending with the
foundation. This includes design load definition, analysis methods, material
strengths and fatigue properties. The level of detail provided here sets the GL rules
apart from the IEC and Danish standards, and is a consequence of their role in
defining the design documentation required for certification.
There is a rigorous treatment of the requirements for the control and safety
systems, and for the associated protection and monitoring devices. The centrality of