Page 239 - Wind Energy Handbook
P. 239
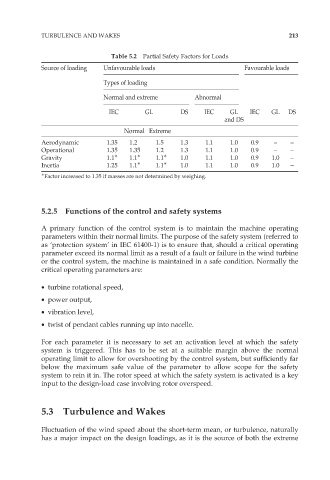
TURBULENCE AND WAKES 213
Table 5.2 Partial Safety Factors for Loads
Source of loading Unfavourable loads Favourable loads
Types of loading
Normal and extreme Abnormal
IEC GL DS IEC GL IEC GL DS
and DS
Normal Extreme
Aerodynamic 1.35 1.2 1.5 1.3 1.1 1.0 0.9 – –
Operational 1.35 1.35 1.2 1.3 1.1 1.0 0.9 – –
Gravity 1.1 1.1 1.1 1.0 1.1 1.0 0.9 1.0 –
Inertia 1.25 1.1 1.1 1.0 1.1 1.0 0.9 1.0 –
Factor increased to 1.35 if masses are not determined by weighing.
5.2.5 Functions of the control and safety systems
A primary function of the control system is to maintain the machine operating
parameters within their normal limits. The purpose of the safety system (referred to
as ‘protection system’ in IEC 61400-1) is to ensure that, should a critical operating
parameter exceed its normal limit as a result of a fault or failure in the wind turbine
or the control system, the machine is maintained in a safe condition. Normally the
critical operating parameters are:
• turbine rotational speed,
• power output,
• vibration level,
• twist of pendant cables running up into nacelle.
For each parameter it is necessary to set an activation level at which the safety
system is triggered. This has to be set at a suitable margin above the normal
operating limit to allow for overshooting by the control system, but sufficiently far
below the maximum safe value of the parameter to allow scope for the safety
system to rein it in. The rotor speed at which the safety system is activated is a key
input to the design-load case involving rotor overspeed.
5.3 Turbulence and Wakes
Fluctuation of the wind speed about the short-term mean, or turbulence, naturally
has a major impact on the design loadings, as it is the source of both the extreme