Page 361 - Wind Energy Handbook
P. 361
MACHINE RATING 335
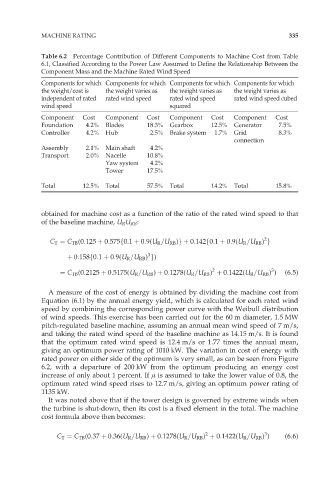
Table 6.2 Percentage Contribution of Different Components to Machine Cost from Table
6.1, Classified According to the Power Law Assumed to Define the Relationship Between the
Component Mass and the Machine Rated Wind Speed
Components for which Components for which Components for which Components for which
the weight/cost is the weight varies as the weight varies as the weight varies as
independent of rated rated wind speed rated wind speed rated wind speed cubed
wind speed squared
Component Cost Component Cost Component Cost Component Cost
Foundation 4.2% Blades 18.3% Gearbox 12.5% Generator 7.5%
Controller 4.2% Hub 2.5% Brake system 1.7% Grid 8.3%
connection
Assembly 2.1% Main shaft 4.2%
Transport 2.0% Nacelle 10.8%
Yaw system 4.2%
Tower 17.5%
Total 12.5% Total 57.5% Total 14.2% Total 15.8%
obtained for machine cost as a function of the ratio of the rated wind speed to that
of the baseline machine, U R U RB :
2
C T ¼ C TB (0:125 þ 0:575f0:1 þ 0:9(U R =U RB )gþ 0:142f0:1 þ 0:9(U R =U RB ) g
3
þ 0:158f0:1 þ 0:9(U R =U RB ) g)
2
3
¼ C TB (0:2125 þ 0:5175(U R =U RB ) þ 0:1278(U R =U RB ) þ 0:1422(U R =U RB ) ) (6:5)
A measure of the cost of energy is obtained by dividing the machine cost from
Equation (6.1) by the annual energy yield, which is calculated for each rated wind
speed by combining the corresponding power curve with the Weibull distribution
of wind speeds. This exercise has been carried out for the 60 m diameter, 1.5 MW
pitch-regulated baseline machine, assuming an annual mean wind speed of 7 m/s,
and taking the rated wind speed of the baseline machine as 14.15 m/s. It is found
that the optimum rated wind speed is 12.4 m/s or 1.77 times the annual mean,
giving an optimum power rating of 1010 kW. The variation in cost of energy with
rated power on either side of the optimum is very small, as can be seen from Figure
6.2, with a departure of 200 kW from the optimum producing an energy cost
increase of only about 1 percent. If ì is assumed to take the lower value of 0.8, the
optimum rated wind speed rises to 12.7 m/s, giving an optimum power rating of
1135 kW.
It was noted above that if the tower design is governed by extreme winds when
the turbine is shut-down, then its cost is a fixed element in the total. The machine
cost formula above then becomes:
3
2
C T ¼ C TB (0:37 þ 0:36(U R =U RB ) þ 0:1278(U R =U RB ) þ 0:1422(U R =U RB ) ) (6:6)