Page 362 - Wind Energy Handbook
P. 362
336 CONCEPTUAL DESIGN OF HORIZONTAL-AXIS TURBINES
110
105
100
Cost index 95
90
85
80
0 250 500 750 1000 1250 1500 1750
Rated power (kW)
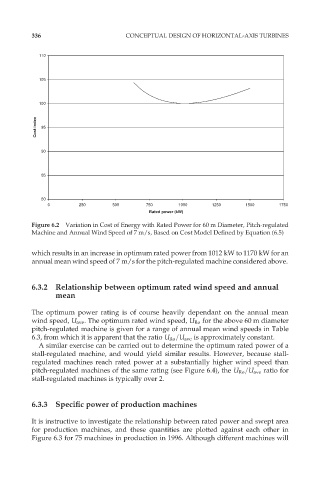
Figure 6.2 Variation in Cost of Energy with Rated Power for 60 m Diameter, Pitch-regulated
Machine and Annual Wind Speed of 7 m/s, Based on Cost Model Defined by Equation (6.5)
which results in an increase in optimum rated power from 1012 kW to 1170 kW for an
annual mean wind speed of 7 m/s for the pitch-regulated machine considered above.
6.3.2 Relationship between optimum rated wind speed and annual
mean
The optimum power rating is of course heavily dependant on the annual mean
wind speed, U ave . The optimum rated wind speed, U Ro for the above 60 m diameter
pitch-regulated machine is given for a range of annual mean wind speeds in Table
6.3, from which it is apparent that the ratio U Ro =U ave is approximately constant.
A similar exercise can be carried out to determine the optimum rated power of a
stall-regulated machine, and would yield similar results. However, because stall-
regulated machines reach rated power at a substantially higher wind speed than
pitch-regulated machines of the same rating (see Figure 6.4), the U Ro =U ave ratio for
stall-regulated machines is typically over 2.
6.3.3 Specific power of production machines
It is instructive to investigate the relationship between rated power and swept area
for production machines, and these quantities are plotted against each other in
Figure 6.3 for 75 machines in production in 1996. Although different machines will