Page 164 - Mechanical Behavior of Materials
P. 164
Section 4.8 Notch-Impact Tests 165
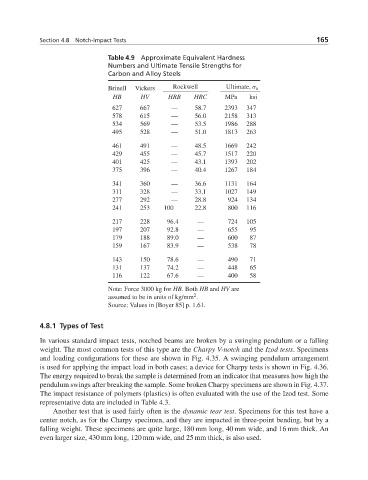
Table 4.9 Approximate Equivalent Hardness
Numbers and Ultimate Tensile Strengths for
Carbon and Alloy Steels
Brinell Vickers Rockwell Ultimate, σ u
HB HV HRB HRC MPa ksi
627 667 — 58.7 2393 347
578 615 — 56.0 2158 313
534 569 — 53.5 1986 288
495 528 — 51.0 1813 263
461 491 — 48.5 1669 242
429 455 — 45.7 1517 220
401 425 — 43.1 1393 202
375 396 — 40.4 1267 184
341 360 — 36.6 1131 164
311 328 — 33.1 1027 149
277 292 — 28.8 924 134
241 253 100 22.8 800 116
217 228 96.4 — 724 105
197 207 92.8 — 655 95
179 188 89.0 — 600 87
159 167 83.9 — 538 78
143 150 78.6 — 490 71
131 137 74.2 — 448 65
116 122 67.6 — 400 58
Note: Force 3000 kg for HB.Both HB and HV are
2
assumed to be in units of kg/mm .
Source: Values in [Boyer 85] p. 1.61.
4.8.1 Types of Test
In various standard impact tests, notched beams are broken by a swinging pendulum or a falling
weight. The most common tests of this type are the Charpy V-notch and the Izod tests. Specimens
and loading configurations for these are shown in Fig. 4.35. A swinging pendulum arrangement
is used for applying the impact load in both cases; a device for Charpy tests is shown in Fig. 4.36.
The energy required to break the sample is determined from an indicator that measures how high the
pendulum swings after breaking the sample. Some broken Charpy specimens are shown in Fig. 4.37.
The impact resistance of polymers (plastics) is often evaluated with the use of the Izod test. Some
representative data are included in Table 4.3.
Another test that is used fairly often is the dynamic tear test. Specimens for this test have a
center notch, as for the Charpy specimen, and they are impacted in three-point bending, but by a
falling weight. These specimens are quite large, 180 mm long, 40 mm wide, and 16 mm thick. An
even larger size, 430 mm long, 120 mm wide, and 25 mm thick, is also used.