Page 295 - Mechanical Behavior of Materials
P. 295
296 Chapter 7 Yielding and Fracture under Combined Stresses
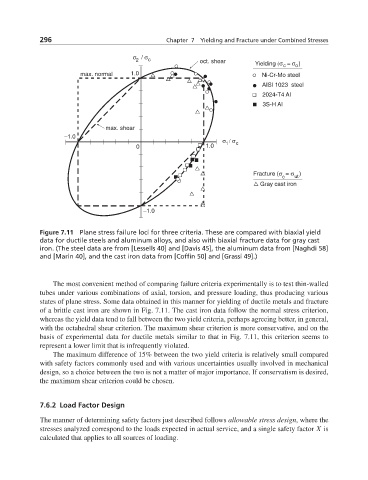
σ / σ
2 c oct. shear
Yielding (σ = σ )
c o
max. normal 1.0 Ni-Cr-Mo steel
AISI 1023 steel
2024-T4 Al
3S-H Al
max. shear
–1.0
σ / σ c
1
0 1.0
Fracture (σ = σ )
c ut
Gray cast iron
–1.0
Figure 7.11 Plane stress failure loci for three criteria. These are compared with biaxial yield
data for ductile steels and aluminum alloys, and also with biaxial fracture data for gray cast
iron. (The steel data are from [Lessells 40] and [Davis 45], the aluminum data from [Naghdi 58]
and [Marin 40], and the cast iron data from [Coffin 50] and [Grassi 49].)
The most convenient method of comparing failure criteria experimentally is to test thin-walled
tubes under various combinations of axial, torsion, and pressure loading, thus producing various
states of plane stress. Some data obtained in this manner for yielding of ductile metals and fracture
of a brittle cast iron are shown in Fig. 7.11. The cast iron data follow the normal stress criterion,
whereas the yield data tend to fall between the two yield criteria, perhaps agreeing better, in general,
with the octahedral shear criterion. The maximum shear criterion is more conservative, and on the
basis of experimental data for ductile metals similar to that in Fig. 7.11, this criterion seems to
represent a lower limit that is infrequently violated.
The maximum difference of 15% between the two yield criteria is relatively small compared
with safety factors commonly used and with various uncertainties usually involved in mechanical
design, so a choice between the two is not a matter of major importance. If conservatism is desired,
the maximum shear criterion could be chosen.
7.6.2 Load Factor Design
The manner of determining safety factors just described follows allowable stress design, where the
stresses analyzed correspond to the loads expected in actual service, and a single safety factor X is
calculated that applies to all sources of loading.