Page 350 - Mechanical Behavior of Materials
P. 350
Section 8.4 Application of K to Design and Analysis 351
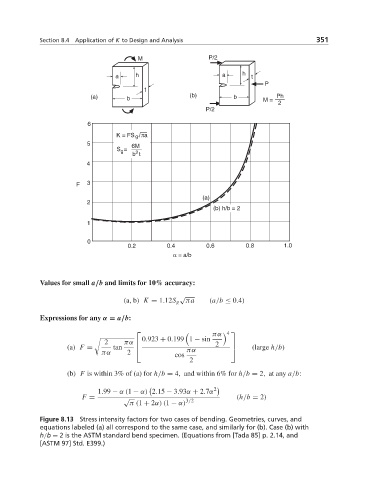
M P/2
a h a h t
P
t
(a) b (b) b M = Ph
2
P/2
6
K = FS πa
g
5 6M
S =
g 2
b t
4
F 3
(a)
2
(b) h/b = 2
1
0
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
α = a/b
Values for small a/b and limits for 10% accuracy:
√
(a, b) K = 1.12S g πa (a/b ≤ 0.4)
Expressions for any α = a/b:
πα 4
⎡ ⎤
0.923 + 0.199 1 − sin
!
2 2
(a) F = tan πα ⎢ πα ⎥ (large h/b)
πα 2 cos
⎣
⎦
2
(b) F is within 3% of (a) for h/b = 4, and within 6% for h/b = 2, at any a/b:
2
1.99 − α (1 − α) 2.15 − 3.93α + 2.7α
F = √ 3/2 (h/b = 2)
π (1 + 2α)(1 − α)
Figure 8.13 Stress intensity factors for two cases of bending. Geometries, curves, and
equations labeled (a) all correspond to the same case, and similarly for (b). Case (b) with
h/b = 2 is the ASTM standard bend specimen. (Equations from [Tada 85] p. 2.14, and
[ASTM 97] Std. E399.)