Page 327 - Introduction to Statistical Pattern Recognition
P. 327
7 Nonparametric Classification and Error Estimation 309
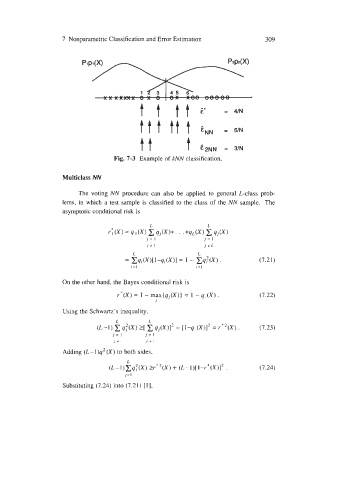
t t ttc = 4/N
tt t e2NN = 3/N
Fig. 7-3 Example of kNN classification.
Multiclass NN
The voting NN procedure can also be applied to general L-class prob-
lems, in which a test sample is classified to the class of the NN sample. The
asymptotic conditional risk is
L L
4 (XI = 9 I (X) s;(X)+. . . +9L(X) c q;(X)
;=I ;=I
jt I ;#L
L L
= cq;(X)[l-qi(X)I = 1 - Zq?(X). (7.21)
i=l i=l
On the other hand, the Bayes conditional risk is
.
I-*(x) = I - max{q,(X)j = 1 - q,(x) (7.22)
J
Using the Schwanz's inequality,
L L
(L-1) qj(X) 2[ 2 q;(X)I2 = [1-q;(X)I2 = r.*2(X) . (7.23)
;=1 j= I
j ti j t;
Adding (L -l)q2 (X) to both sides,
L
(L-l)xq;(x) >I-"*(X) + (L-l)[I-,.*(x)p (7.24)
/=I
Substituting (7.24) into (7.21) [I],