Page 108 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 108
92 3 Life Cycle Inventory Analysis
3.3
Allocation
3.3.1
Fundamentals of Allocation
Allocation means the attribution of environmental burdens during the life cycle,
for co-production, recycling and disposal. In doing so, however, fundamental
problems of science theory that have not yet been addressed occur, because the
focus until now has been the firm scientific and technical methodology of LCI (for
77)
an exceptionally clear presentation of the fundamentals of LCI see Boguski ):
• validity of the basic laws of physics and chemistry;
• efficiency parameters of technical plants, agricultural processes, and so on;
• clear and unambiguous cut-off criteria.
Limits to a strict scientific-technical analysis are reached for the first time
when attributing environmental burdens in the ‘upper’ part of the product tree
for a simultaneous production of several products in one unit process. 78) This is best
demonstrated in the case of co-production.
3.3.2
Allocation by the Example of Co-production
3.3.2.1 Definition of Co-production
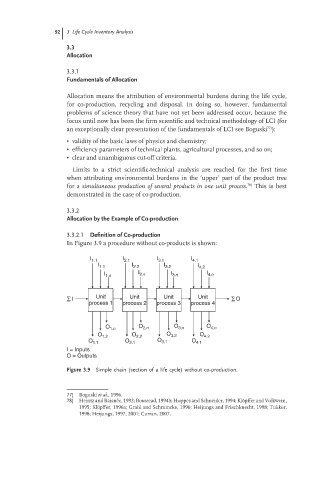
In Figure 3.9 a procedure without co-products is shown:
I 1.1 I 2.1 I 3.1 I 4.1
I 1.1 I 2.2 I 3.2 I 4.2
I 1.n I 2.n I 3.n I 4.n
∑I Unit Unit Unit Unit ∑O
process 1 process 2 process 3 process 4
O 1.n O 2.n O 3.n O 4.n
O 1.2 O 2.2 O 3.2 O 4.2
O 1.1 O 2.1 O 3.1 O 4.1
I = Inputs
O = Outputs
Figure 3.9 Simple chain (section of a life cycle) without co-production.
77) Boguski et al., 1996.
78) Heintz and Baisn´ ee, 1992; Boustead, 1994b; Huppes and Schneider, 1994; Kl¨ opffer and Volkwein,
1995; Kl¨ opffer, 1996a; Grahl and Schmincke, 1996; Heijungs and Frischknecht, 1998; Tukker,
1998; Heijungs, 1997, 2001; Curran, 2007.