Page 120 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 120
104 3 Life Cycle Inventory Analysis
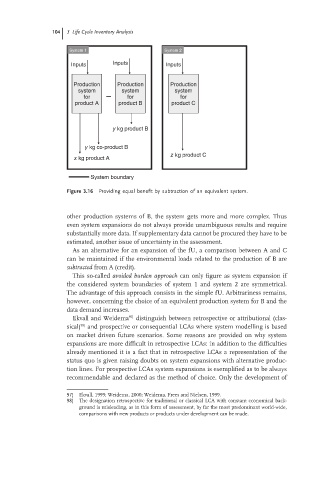
System 1 System 2
Inputs Inputs Inputs
Production Production Production
system system system
for for for
product A product B product C
y kg product B
y kg co-product B
z kg product C
x kg product A
System boundary
Figure 3.16 Providing equal benefit by subtraction of an equivalent system.
other production systems of B, the system gets more and more complex. Thus
even system expansions do not always provide unambiguous results and require
substantially more data. If supplementary data cannot be procured they have to be
estimated, another issue of uncertainty in the assessment.
As an alternative for an expansion of the fU, a comparison between A and C
can be maintained if the environmental loads related to the production of B are
subtracted fromA(credit).
This so-called avoided burden approach can only figure as system expansion if
the considered system boundaries of system 1 and system 2 are symmetrical.
The advantage of this approach consists in the simple fU. Arbitrariness remains,
however, concerning the choice of an equivalent production system for B and the
data demand increases.
Ekvall and Weidema 97) distinguish between retrospective or attributional (clas-
sical) 98) and prospective or consequential LCAs where system modelling is based
on market driven future scenarios. Some reasons are provided on why system
expansions are more difficult in retrospective LCAs: in addition to the difficulties
already mentioned it is a fact that in retrospective LCAs a representation of the
status quo is given raising doubts on system expansions with alternative produc-
tion lines. For prospective LCAs system expansions is exemplified as to be always
recommendable and declared as the method of choice. Only the development of
97) Ekvall, 1999; Weidema, 2000; Weidema, Frees and Nielsen, 1999.
98) The designation retrospective for traditional or classical LCA with constant economical back-
ground is misleading, as in this form of assessment, by far the most predominant world-wide,
comparisons with new products or products under development can be made.