Page 121 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 121
3.3 Allocation 105
Raw material
extraction
Material production
Pre-production
Closed-loop
recycling
Production product x
Use
Recycling Disposal
System boundary
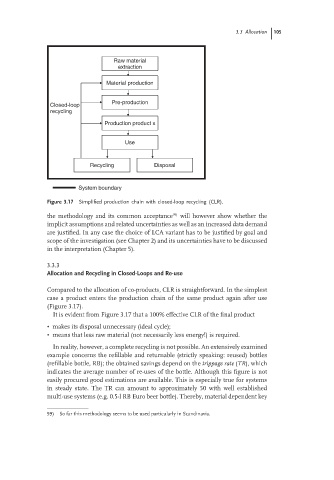
Figure 3.17 Simplified production chain with closed-loop recycling (CLR).
the methodology and its common acceptance 99) will however show whether the
implicit assumptions and related uncertainties as well as an increased data demand
are justified. In any case the choice of LCA variant has to be justified by goal and
scope of the investigation (see Chapter 2) and its uncertainties have to be discussed
in the interpretation (Chapter 5).
3.3.3
Allocation and Recycling in Closed-Loops and Re-use
Compared to the allocation of co-products, CLR is straightforward. In the simplest
case a product enters the production chain of the same product again after use
(Figure 3.17).
It is evident from Figure 3.17 that a 100% effective CLR of the final product
• makes its disposal unnecessary (ideal cycle);
• means that less raw material (not necessarily less energy!) is required.
In reality, however, a complete recycling is not possible. An extensively examined
example concerns the refillable and returnable (strictly speaking: reused) bottles
(refillable bottle, RB); the obtained savings depend on the trippage rate (TR), which
indicates the average number of re-uses of the bottle. Although this figure is not
easily procured good estimations are available. This is especially true for systems
in steady state. The TR can amount to approximately 50 with well established
multi-use systems (e.g. 0.5-l RB Euro beer bottle). Thereby, material dependent key
99) So far this methodology seems to be used particularly in Scandinavia.