Page 126 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 126
110 3 Life Cycle Inventory Analysis
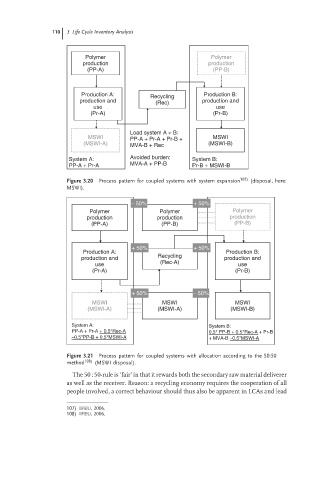
Polymer Polymer
production production
(PP-A) (PP-B)
Production A: Recycling Production B:
production and (Rec) production and
use use
(Pr-A) (Pr-B)
Load system A + B:
MSWI PP-A + Pr-A + Pr-B + MSWI
(MSWI-A) MVA-B + Rec (MSWI-B)
System A: Avoided burden: System B:
PP-A + Pr-A MVA-A + PP-B Pr-B + MSWI-B
Figure 3.20 Process pattern for coupled systems with system expansion 107) (disposal, here:
MSWI).
− 50% + 50%
Polymer Polymer Polymer
production production production
(PP-A) (PP-B) (PP-B)
+ 50% + 50%
Production A: Production B:
production and Recycling production and
use (Rec-A) use
(Pr-A) (Pr-B)
+ 50% − 50%
MSWI MSWI MSWI
(MSWI-A) (MSWI-A) (MSWI-B)
System A: System B:
PP-A + Pr-A + 0.5*Rec-A 0.5* PP-B + 0.5*Rec-A + Pr-B
−0.5*PP-B + 0.5*MSWI-A + MVA-B −0.5*MSWI-A
Figure 3.21 Process pattern for coupled systems with allocation according to the 50:50
method 108) (MSWI disposal).
The 50 : 50-rule is ‘fair’ in that it rewards both the secondary raw material deliverer
as well as the receiver. Reason: a recycling economy requires the cooperation of all
people involved, a correct behaviour should thus also be apparent in LCAs and lead
107) IFEU, 2006.
108) IFEU, 2006.