Page 329 -
P. 329
LIME SOFTENING 11,9
Approx. remaining alkalinity = 35 mg/L as CaCO3
(approx. minimum solubility of CaCO3)t
Approximate CO2 feed requirements remain the same as for Example 11.1.
Excess Lime or Excess Lime-Soda Ash Process
In lime softening, the term excess lime refers to the removal of magnesium, in addition
to calcium, by providing excess lime in the primary softening process. The excess lime
process can generally remove calcium hardness to a level of about 35 mg/L and magne-
sium hardness to about t0 mg/L. Chemical dosage requirements can be estimated by us-
ing Equation (11.9) for the excess lime process and Equations (11.9) and (11.10) for the
excess lime-soda ash process.
Single-Stage Excess Lime or Excess Lime-Soda Ash Process. The single-stage excess
lime or excess lime-soda ash process is similar to Figure 11.1. Excess lime leaving the
softening basin is reacted with additional carbon dioxide in the recarbonation basin to
lower the pH of the water and to stabilize the water before filtration.
Although single-stage excess lime softening plants have been operated successfully,
several problems are commonly encountered. It is more difficult to achieve process sta-
bility with excess lime softening in the typical recarbonation basin, resulting in potential
deposition of calcium carbonate on the filter media. In addition, residuals buildup in the
recarbonation basin creates periodic basin cleaning requirements. Particulate loading to
the filters is high during periods of process instability in the softening basin.
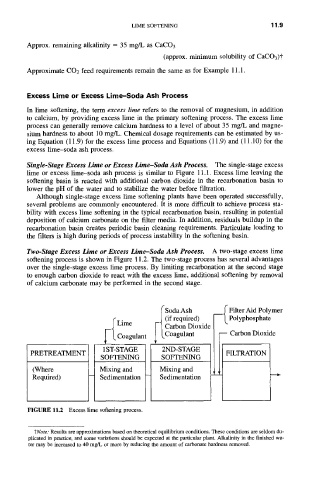
Two-Stage Excess Lime or Excess Lime-Soda Ash Process. A two-stage excess lime
softening process is shown in Figure 11.2. The two-stage process has several advantages
over the single-stage excess lime process. By limiting recarbonation at the second stage
to enough carbon dioxide to react with the excess lime, additional softening by removal
of calcium carbonate may be performed in the second stage.
~ Soda Ash ~ Filter Aid Polymer
-4 (if required) -- L Polyphosphate
f Lime
|Carbon Dioxide
LCoagulant FCarbon Dio._______~xide
Ft. Coagulant
1ST-STAGE 2ND-STAGE
PRETREATMENT ILTRATION
SOFTENING SOFFENING
(Where Mixing and Mixing and
Required) Sedimentation Sedimentation
FIGURE 11.2 Excess lime softening process.
tNote: Results are approximations based on theoretical equilibrium conditions. These conditions are seldom du-
plicated in practice, and some variations should be expected at the particular plant. Alkalinity in the finished wa-
ter may be increased to 40 mg/L or more by reducing the amount of carbonate hardness removed.