Page 225 - 15 Dangerously Mad Projects for the Evil Genius
P. 225
Chapter 15 ■ Surveillance Robot 201
milliseconds and forwardOrProximity moves Another effect of this design is that the sensor is
forward for the time specified in its argument, or not linear, but rather follows a parabolic curve.
until the proximity sensor detects an obstacle. If an Fortunately for us, we just want to know when we
obstacle is detected, the robot buzzes twice and are close to an obstacle, not how far away it is.
then reverses.
Driving Motors
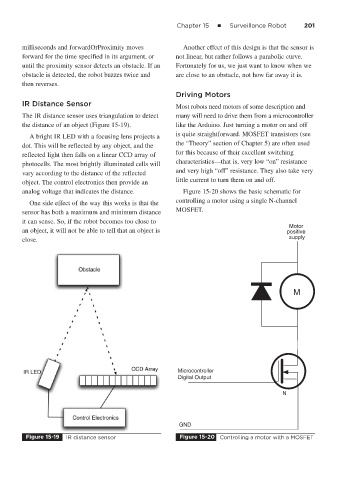
IR Distance Sensor Most robots need motors of some description and
The IR distance sensor uses triangulation to detect many will need to drive them from a microcontroller
the distance of an object (Figure 15-19). like the Arduino. Just turning a motor on and off
A bright IR LED with a focusing lens projects a is quite straightforward. MOSFET transistors (see
the “Theory” section of Chapter 5) are often used
dot. This will be reflected by any object, and the
for this because of their excellent switching
reflected light then falls on a linear CCD array of
characteristics—that is, very low “on” resistance
photocells. The most brightly illuminated cells will
and very high “off” resistance. They also take very
vary according to the distance of the reflected
little current to turn them on and off.
object. The control electronics then provide an
analog voltage that indicates the distance. Figure 15-20 shows the basic schematic for
controlling a motor using a single N-channel
One side effect of the way this works is that the
MOSFET.
sensor has both a maximum and minimum distance
it can sense. So, if the robot becomes too close to
Motor
an object, it will not be able to tell that an object is positive
close. supply
M
Microcontroller
Digital Output
N
GND
Figure 15-19 IR distance sensor Figure 15-20 Controlling a motor with a MOSFET