Page 143 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 143
132 30 Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
binders are more effective in improving the delamination resistance for mode I than
mode I1 loading. This is shown in Figure 5.24 that compares improvements to the
modes I and I1 interlaminar fracture toughness values for the same 3D woven
composite. It is seen that the mode I toughness of the 3D composite is -14 times higher
than the 2D laminate whereas the mode I1 toughness is only 2.7 times higher.
-
1.4
-
2 1.2
Y,
-0
(d -
4 1.0
t
.-
0
.c.
.E 0.8 -
5
-
a,
0 -
0.6
0.4- ' I * ' * I ' I '
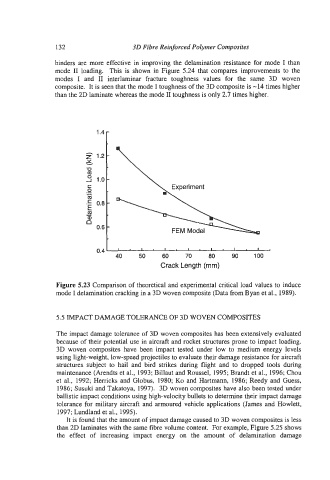
Figure 5.23 Comparison of theoretical and experimental critical load values to induce
mode I delamination cracking in a 3D woven composite (Data from Byan et al., 1989).
5.5 IMPACT DAMAGE TOLERANCE OF 3D WOVEN COMPOSITES
The impact damage tolerance of 3D woven composites has been extensively evaluated
because of their potential use in aircraft and rocket structures prone to impact loading.
3D woven composites have been impact tested under low to medium energy levels
using light-weight, low-speed projectiles to evaluate their damage resistance for aircraft
structures subject to hail and bird strikes during flight and to dropped tools during
maintenance (Arendts et al., 1993; Billaut and Roussel, 1995; Brandt et al., 1996; Chou
et al., 1992; Herricks and Globus, 1980; KO and Hartmann, 1986; Reedy and Guess,
1986; Susuki and Takatoya, 1997). 3D woven composites have also been tested under
ballistic impact conditions using high-velocity bullets to determine their impact damage
tolerance for military aircraft and armoured vehicle applications (James and Howlett,
1997; Lundland et al., 1995).
It is found that the amount of impact damage caused to 3D woven composites is less
than 2D laminates with the same fibre volume content. For example, Figure 5.25 shows
the effect of increasing impact energy on the amount of delamination damage